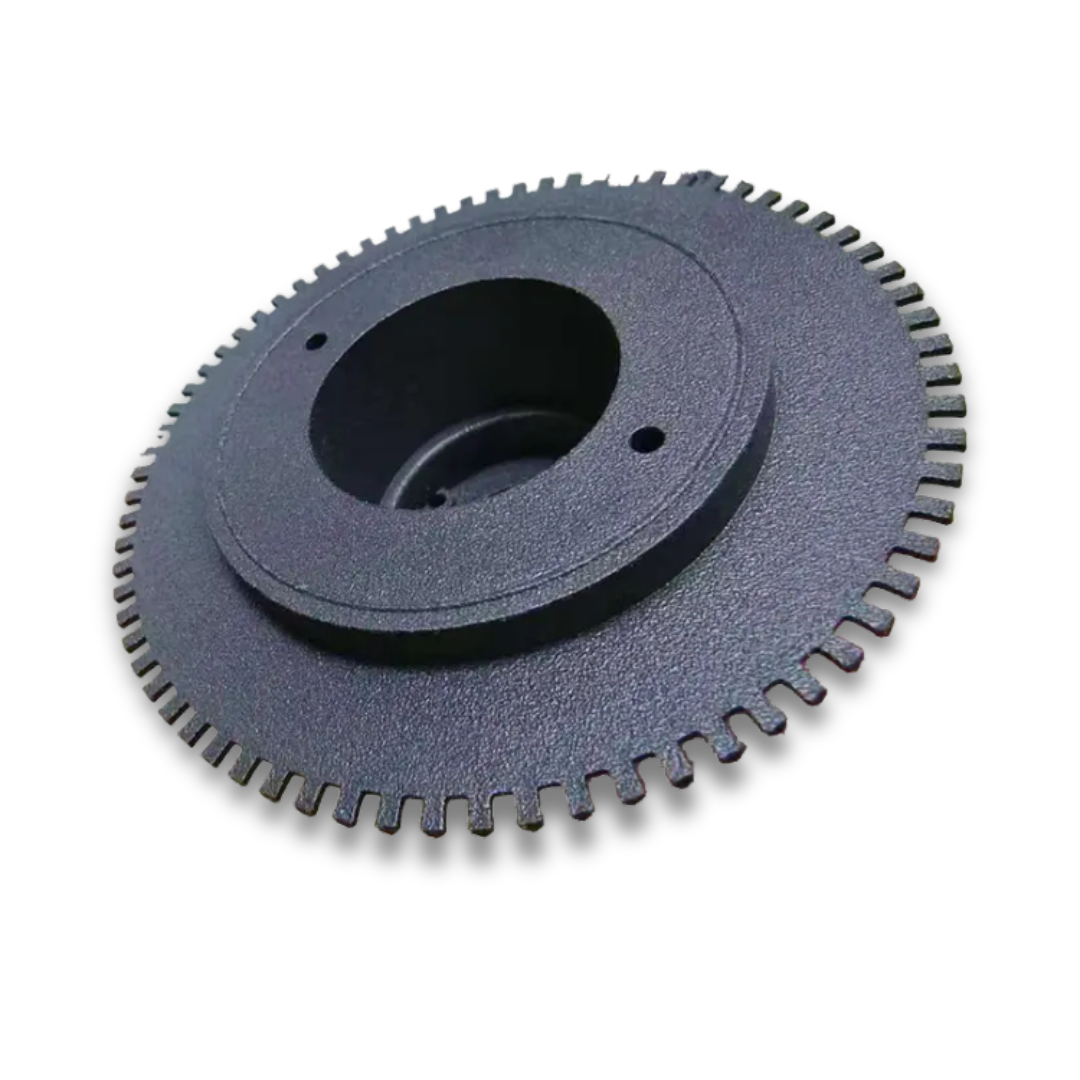
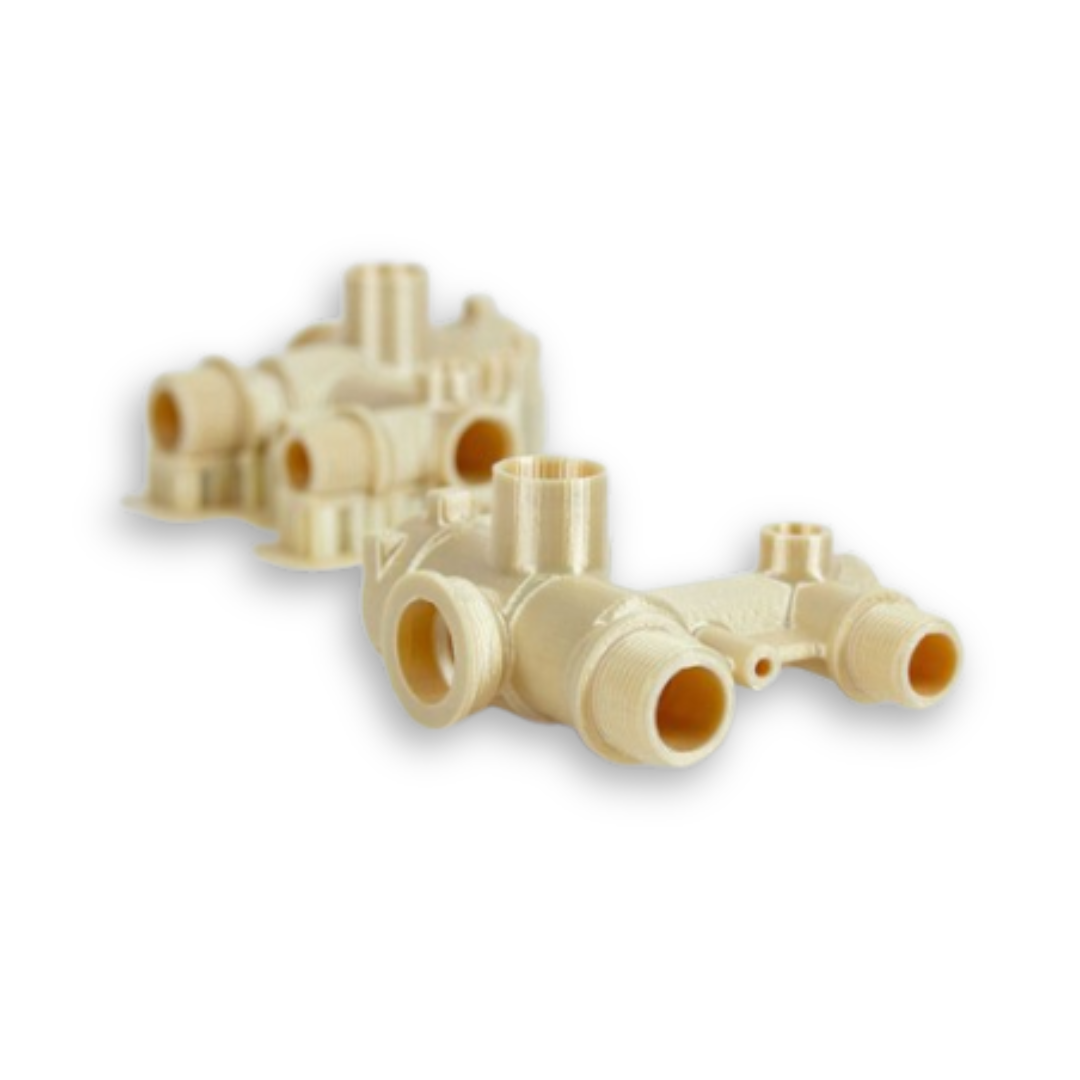
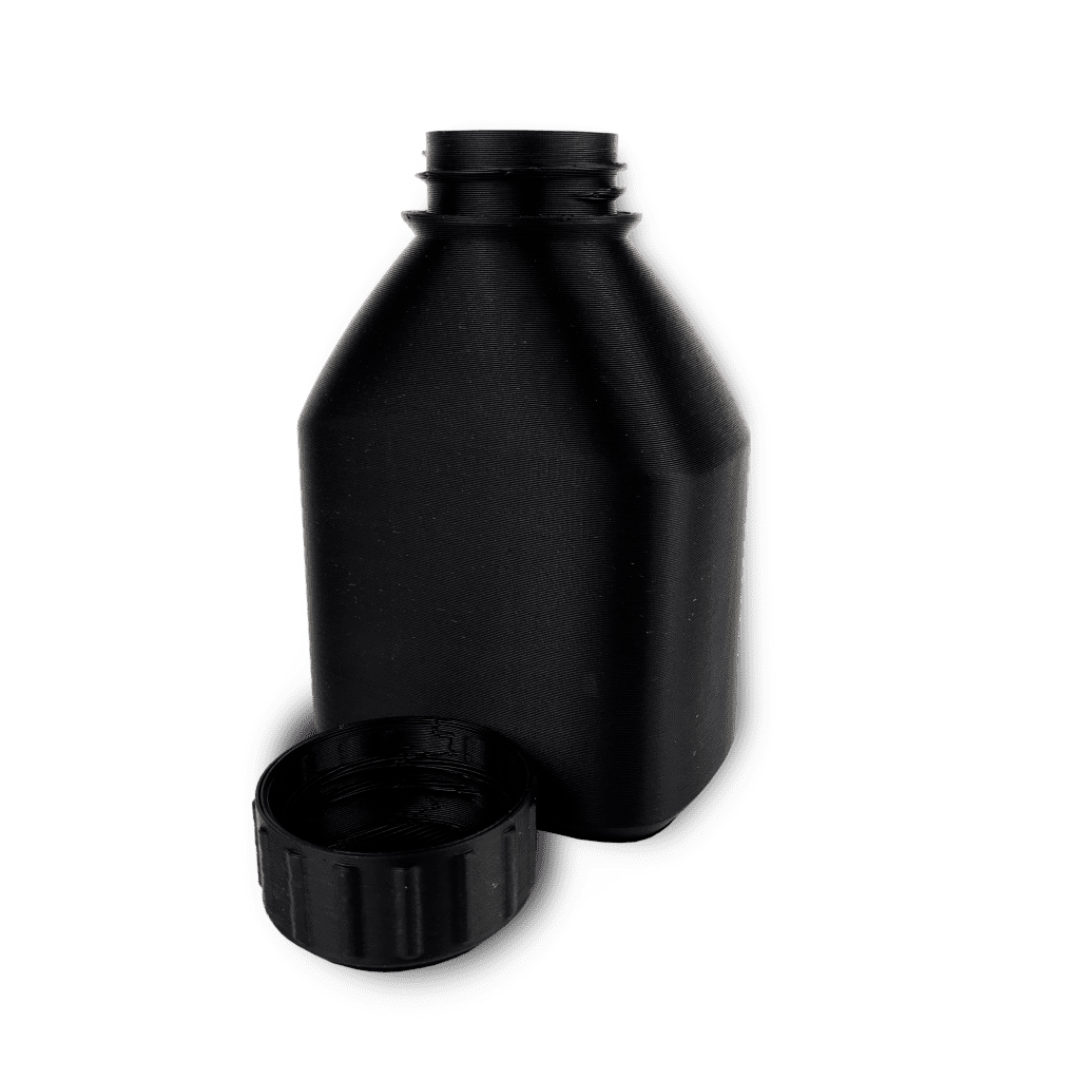
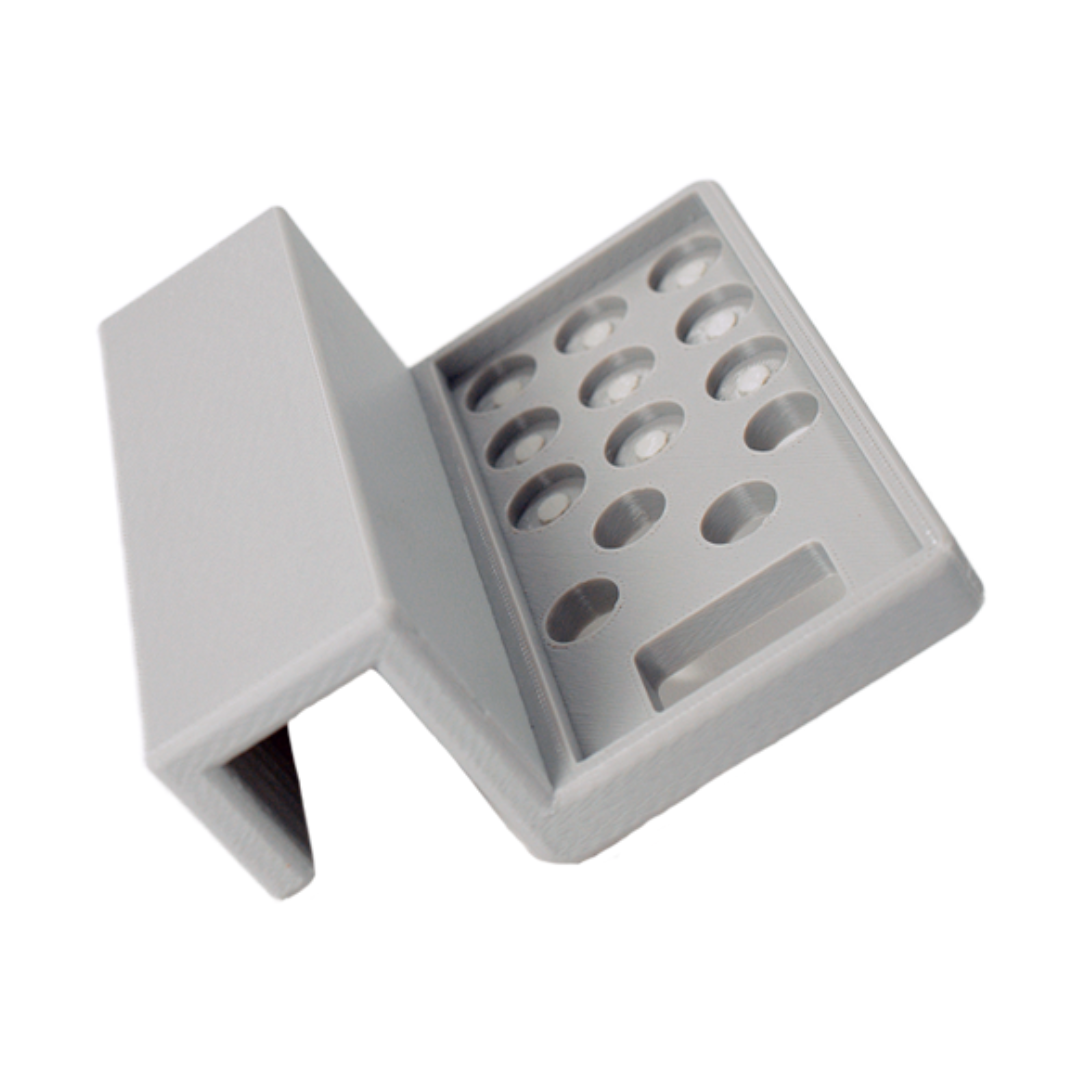
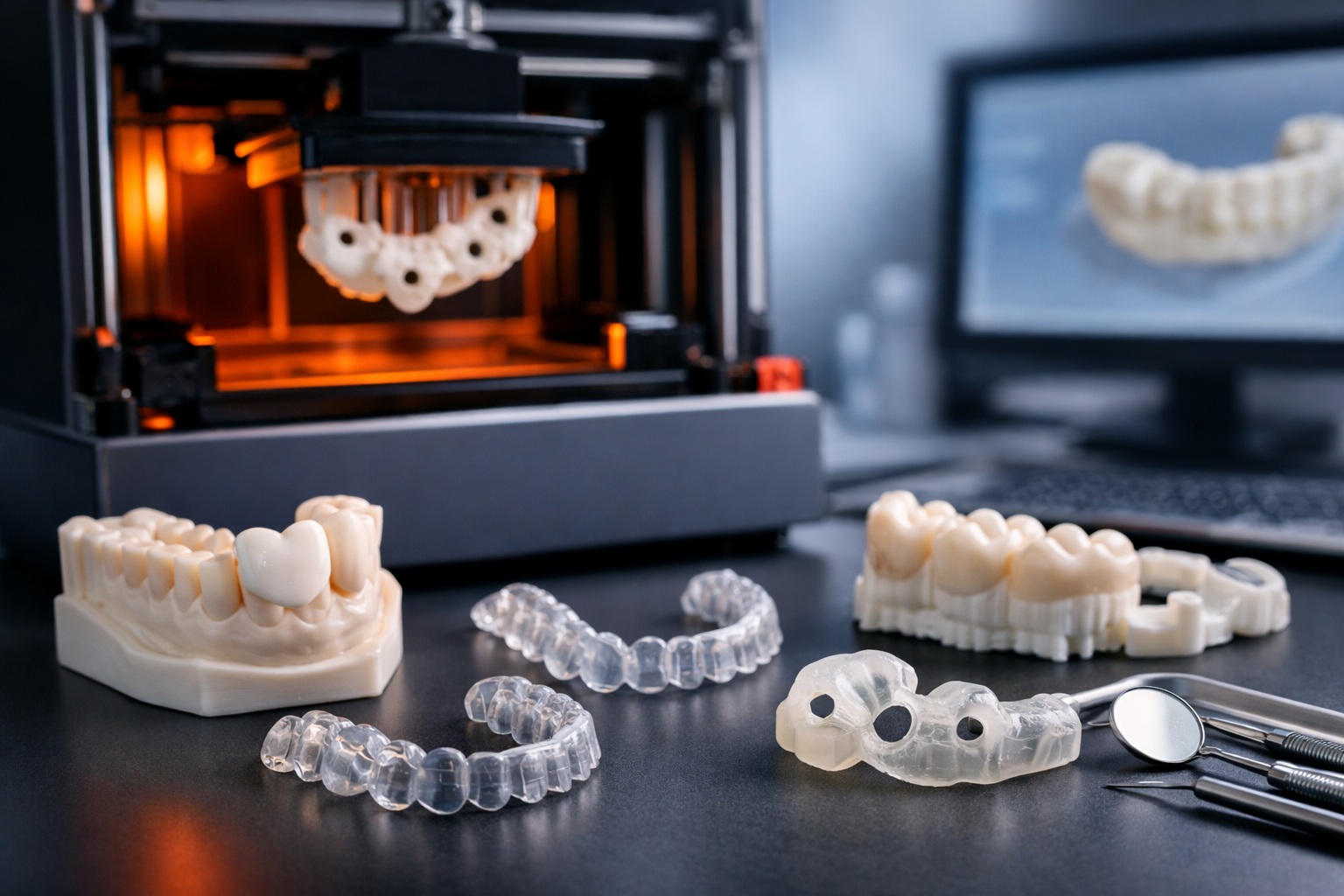
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) : Additive Manufacturing Technology
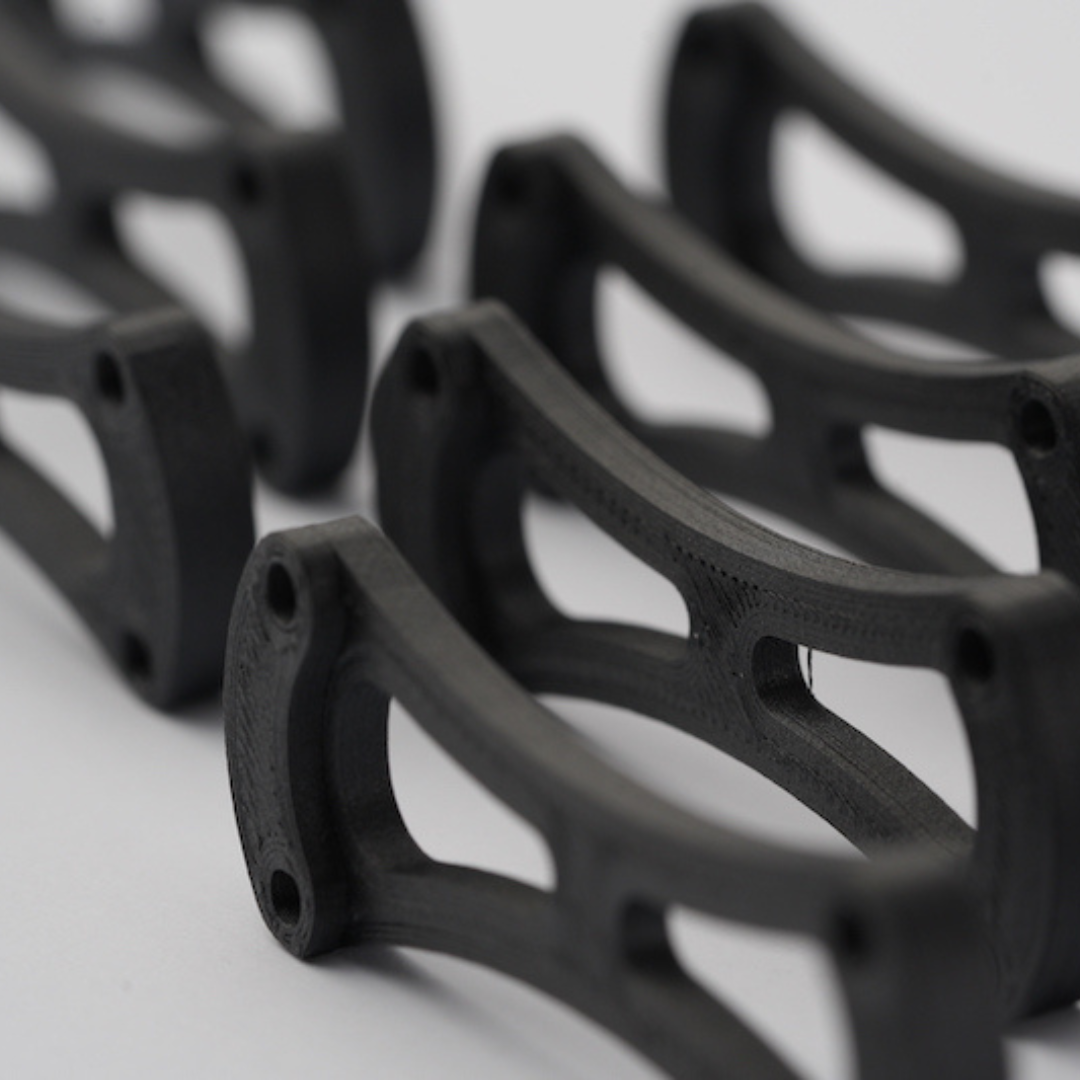
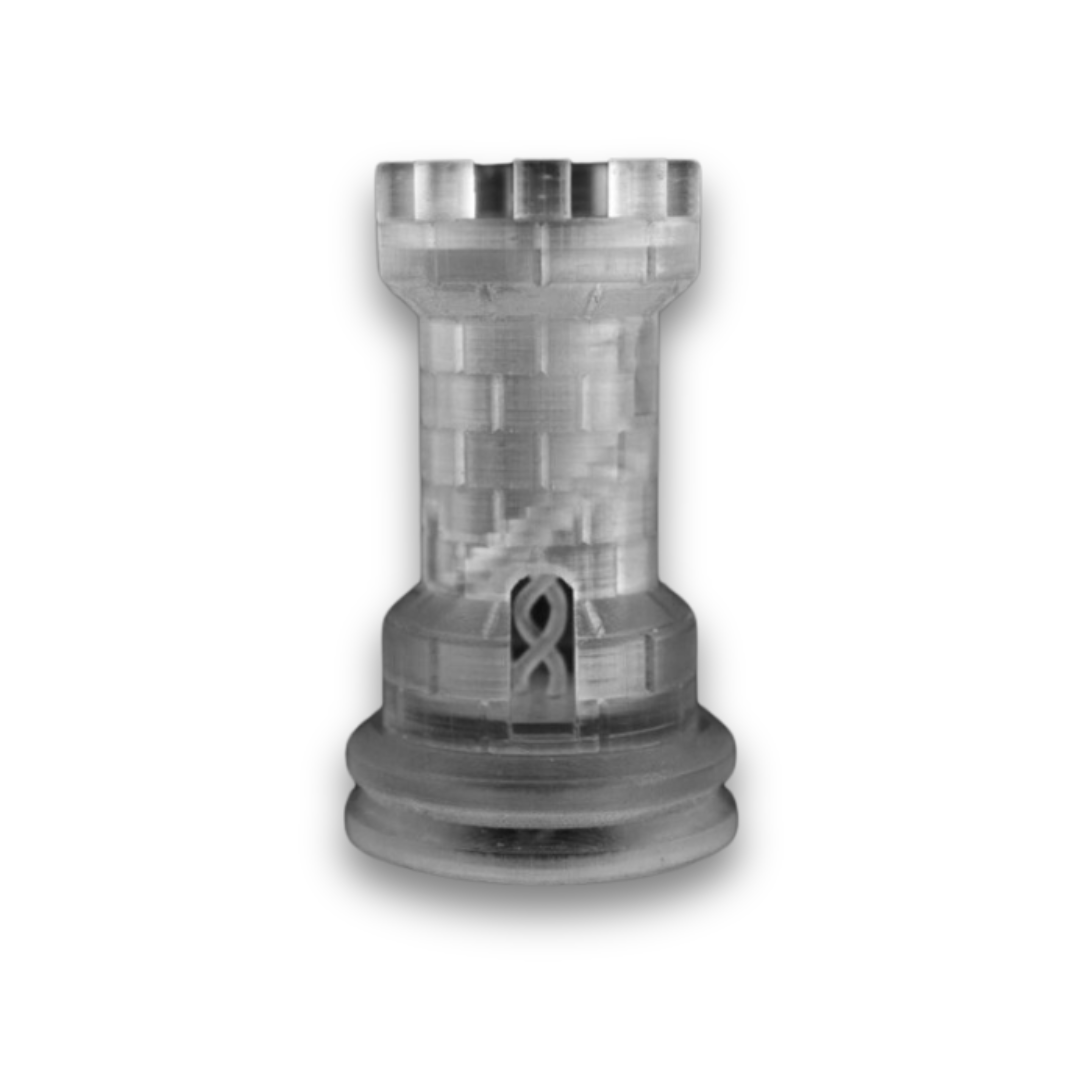
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is one of the most popular additive manufacturing technologies, commonly known as 3D printing. Unlike traditional subtractive manufacturing methods like machining, which remove material to create an object, FDM builds parts layer by layer using thermoplastic materials. This innovative approach allows for the creation of complex geometries and internal structures that would be impossible or costly to produce with conventional methods.
FDM is widely used across industries for prototyping, tooling, and even end-use parts due to its versatility, cost-effectiveness, and ease of use.
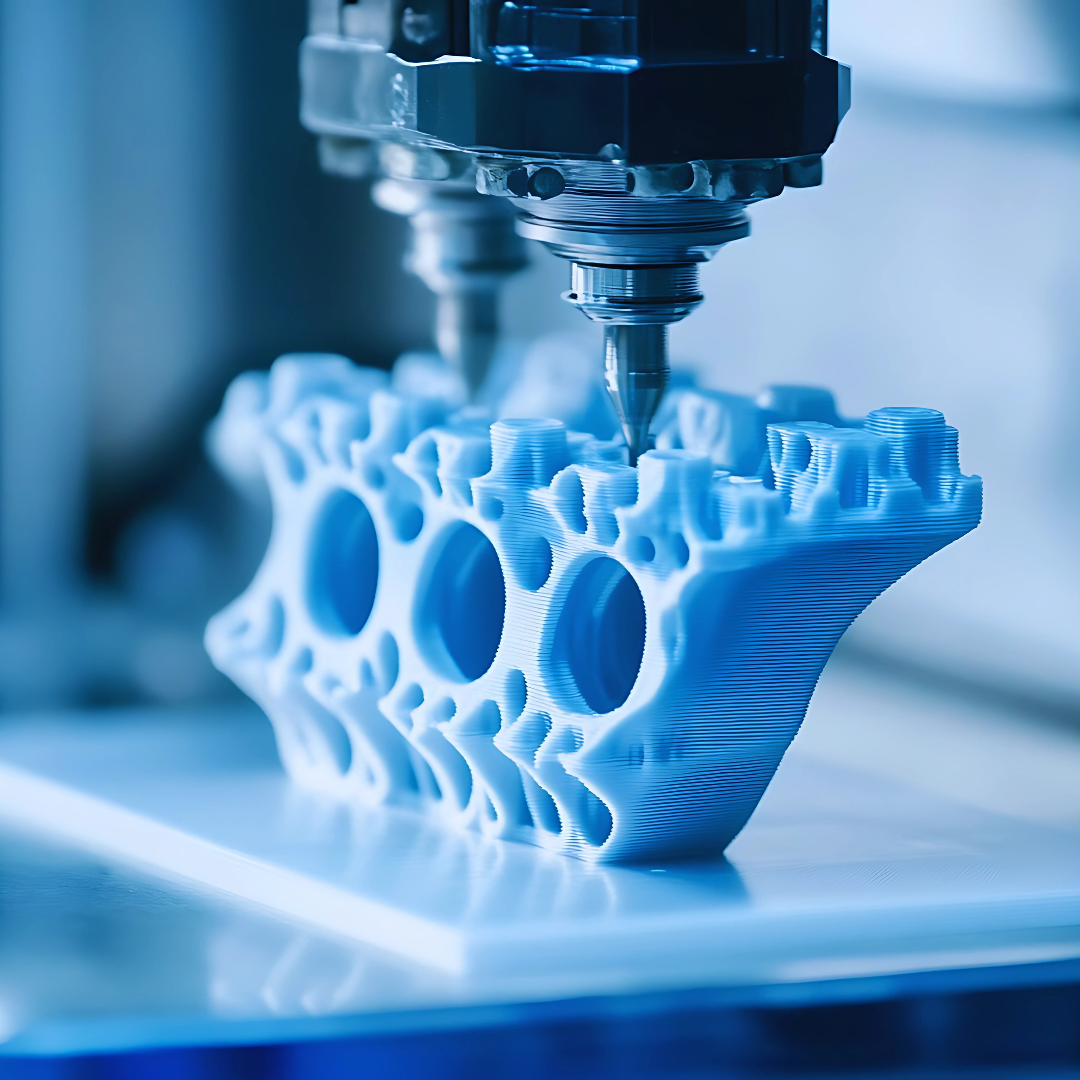

How Does FDM Work?
The FDM process involves the following steps:
Material Feeding: A thermoplastic filament (e.g., ABS, PLA) is fed into a heated nozzle.
Melting and Extrusion: The nozzle heats the filament to its melting point and extrudes it onto a build platform.
Layer-by-Layer Deposition: The material is deposited in thin layers, which solidify quickly to form a 3D object.
Support Structures: For overhangs or complex geometries, support structures are printed and later removed.
Post-Processing: The finished part may require sanding, painting, or other finishing touches.
FDM is known for its simplicity and reliability, making it a favorite among hobbyists, engineers, and manufacturers alike.
Key Advantages of FDM Technology
FDM offers several benefits that make it a standout choice in additive manufacturing:
Cost-Effective Solution
FDM is one of the most affordable 3D printing technologies, making it ideal for businesses and individuals with budget constraints. The materials (thermoplastics) are relatively inexpensive, and the machines are widely available at various price points.Wide Range of Materials
FDM supports a variety of thermoplastic materials, each with unique properties to suit different applications. Common materials include:PLA: Easy to use, biodegradable, and great for prototypes.
ABS: Durable, impact-resistant, and suitable for functional parts.
PETG: Strong, flexible, and resistant to chemicals and moisture.
TPU: Flexible and ideal for rubber-like parts.
Nylon: High strength, durability, and resistance to wear.
User-Friendly Technology
FDM printers are easy to operate, even for beginners. With intuitive software and minimal setup requirements, you can start printing quickly without extensive training.Rapid Prototyping
FDM is perfect for creating prototypes quickly and cost-effectively. It allows you to test and iterate designs in a fraction of the time and cost of traditional manufacturing methods.Functional End-Use Parts
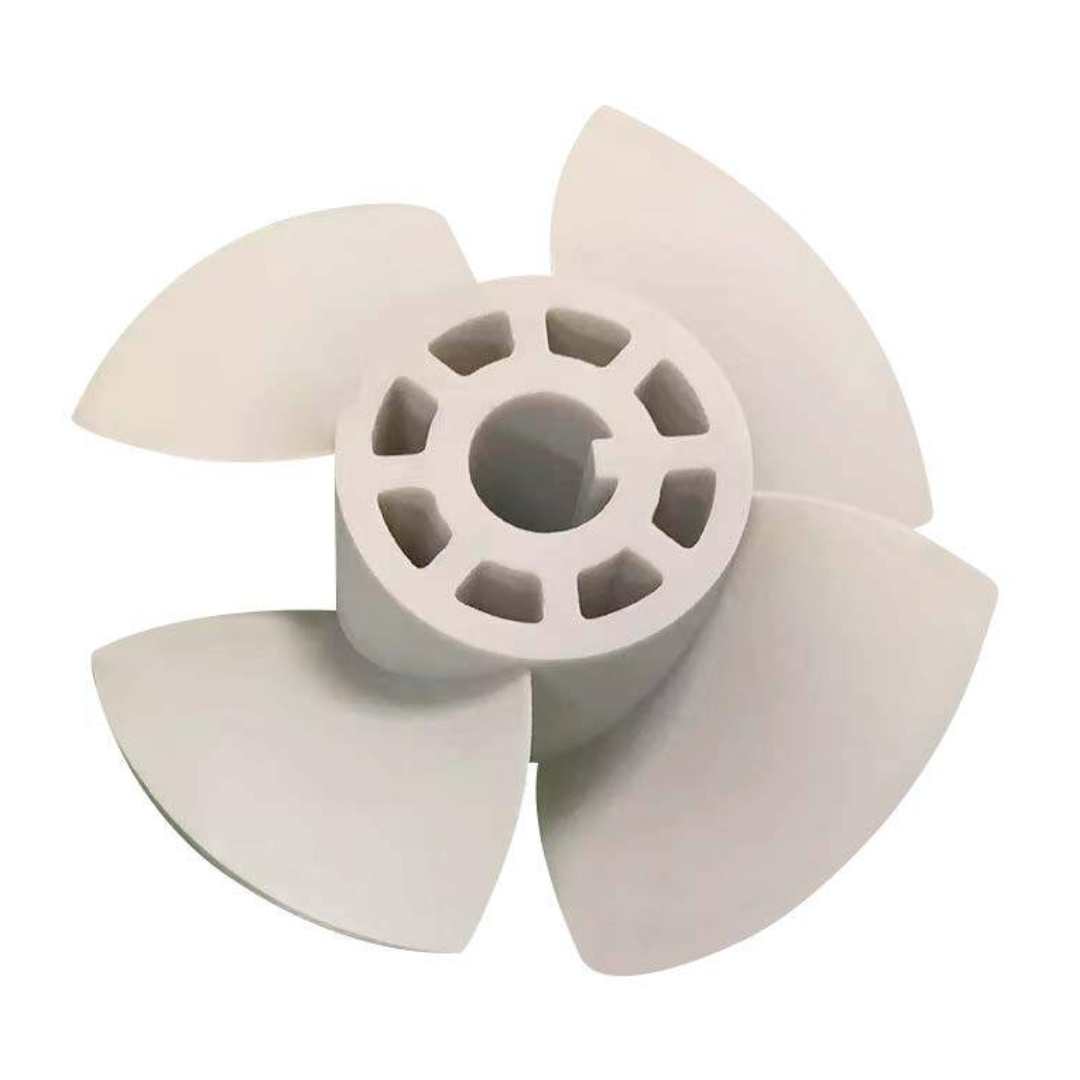
With the right material and settings, FDM can produce durable, functional parts suitable for end-use applications. This makes it a great choice for custom tools, jigs, fixtures, and replacement parts.Scalability and Accessibility
FDM printers are available in a wide range of sizes, from desktop models for small projects to industrial-grade machines for large-scale production. This scalability makes FDM suitable for both personal and professional use.Minimal Waste
FDM is an additive manufacturing process, meaning it only uses the material needed to build the part. This reduces waste compared to subtractive methods like CNC machining.
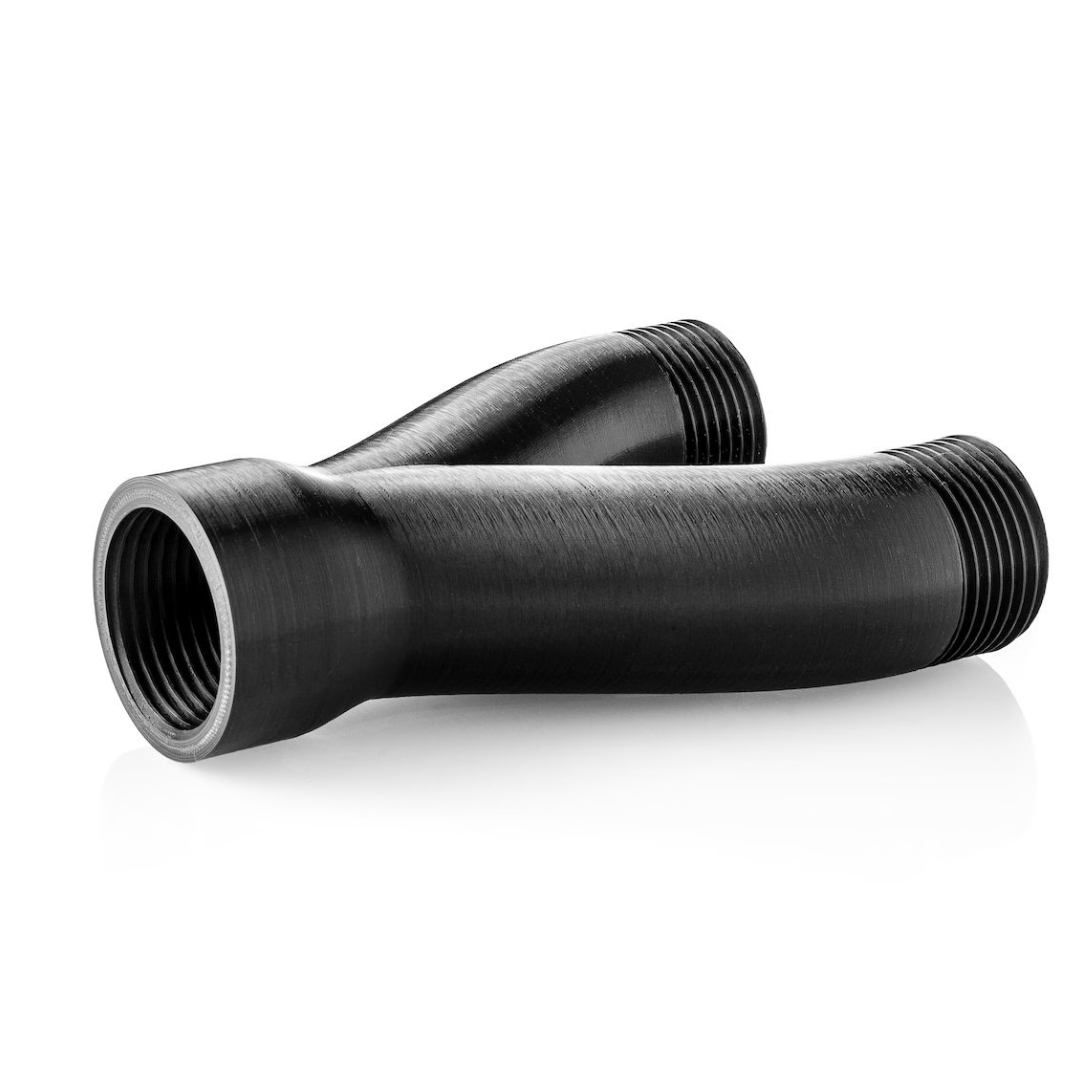

Applications of FDM in Various Industries
FDM is transforming industries with its ability to produce high-quality parts quickly and affordably. Here are some key applications:
- Prototyping: Rapid production of functional prototypes for design validation.
- Aerospace: Lightweight, durable components for aircraft and spacecraft.
- Automotive: Custom tools, jigs, and end-use parts.
- Healthcare: Prosthetics, surgical guides, and medical devices.
- Education: Teaching tool for engineering and design students.
- Consumer Goods: Customized products and small-batch manufacturing.
Materials Used in FDM
FDM technology supports a variety of thermoplastics, each with unique properties:
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): Strong, durable, and heat-resistant.
PLA (Polylactic Acid): Biodegradable, easy to print, and ideal for prototypes.
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol): Combines strength, flexibility, and chemical resistance.
Nylon: Lightweight, tough, and wear-resistant.
TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane): Flexible and elastic, perfect for rubber-like parts.
These materials make FDM suitable for a wide range of applications, from prototyping to end-use parts.

FDM vs. Traditional Manufacturing
FDM offers several advantages over traditional manufacturing methods like machining and injection molding:
Additive vs. Subtractive: FDM adds material only where needed, reducing waste.
Complexity: FDM can create intricate designs that are difficult or impossible with traditional methods.
Cost: Ideal for low-volume production and custom parts.
Speed: Faster turnaround times for prototypes and small batches.
However, traditional methods still excel in high-volume production and ultra-high precision applications.

Future Trends in FDM Technology
The future of FDM is bright, with several exciting advancements on the horizon:
Advanced Materials: Development of high-performance thermoplastics for demanding applications.
Faster Printing: Improved print speeds and larger build volumes.
Hybrid Manufacturing: Combining FDM with other technologies like CNC machining.
Sustainability: Increased use of biodegradable and recycled materials.
AI and IoT Integration: Smart printers with real-time monitoring and optimization.
As FDM technology continues to evolve, it will play an even greater role in industries like healthcare, construction, and aerospace.
Why Choose FDM for Your Next Project?
When it comes to 3D printing technologies, Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) stands out as one of the most popular and accessible options. Known for its versatility, affordability, and ease of use, FDM is an excellent choice for a wide range of applications—from prototyping to end-use parts. Whether you’re a business looking to streamline production or an individual bringing a creative idea to life, FDM offers unmatched flexibility and efficiency. Here’s why FDM should be your go-to technology for your next project.
Why Choose Projet for 3D Printing in Malaysia?
Expert Collaboration for Optimal Results
At Projet, we work closely with you to understand your HMLV manufacturing needs. Our team helps you choose the best materials and optimize build orientation to ensure your parts are produced with precision and efficiency.Wide Range of Materials
Explore our 3D Printing Materials Guide to discover a variety of plastic and metal materials across different technologies. From durable ABS and nylon to high-performance metals like titanium and aluminum, we have the perfect material for your application.State-of-the-Art Technology
We leverage the latest in additive manufacturing technology to deliver high-quality, reliable parts that meet the demands of HMLV production.Nationwide Reach
No matter where you are in Malaysia—be it Kuala Lumpur, Penang, Johor Bahru, or beyond—Projet is your go-to partner for 3D printing services.
3D Printing Service Malaysia , 3D Printing service Singapore , 3D Printing service KL , 3D Printing service Selangor, 3D Scanning Malaysia
Collaborate with 3D printing bureau to choose the best material and optimize build orientation for your project’s needs. Explore our 3D Printing Materials Guide to learn about various plastic and metal materials across technologies.
Discover more about additive manufacturing at projet.my. For assistance, reach out to our applications engineer at enquiry@projettech.com or try our instant quote for immediate pricing feedback.