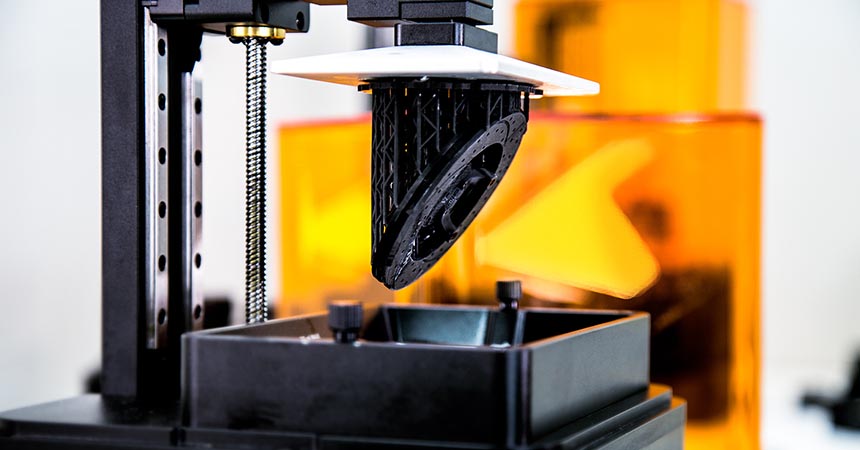
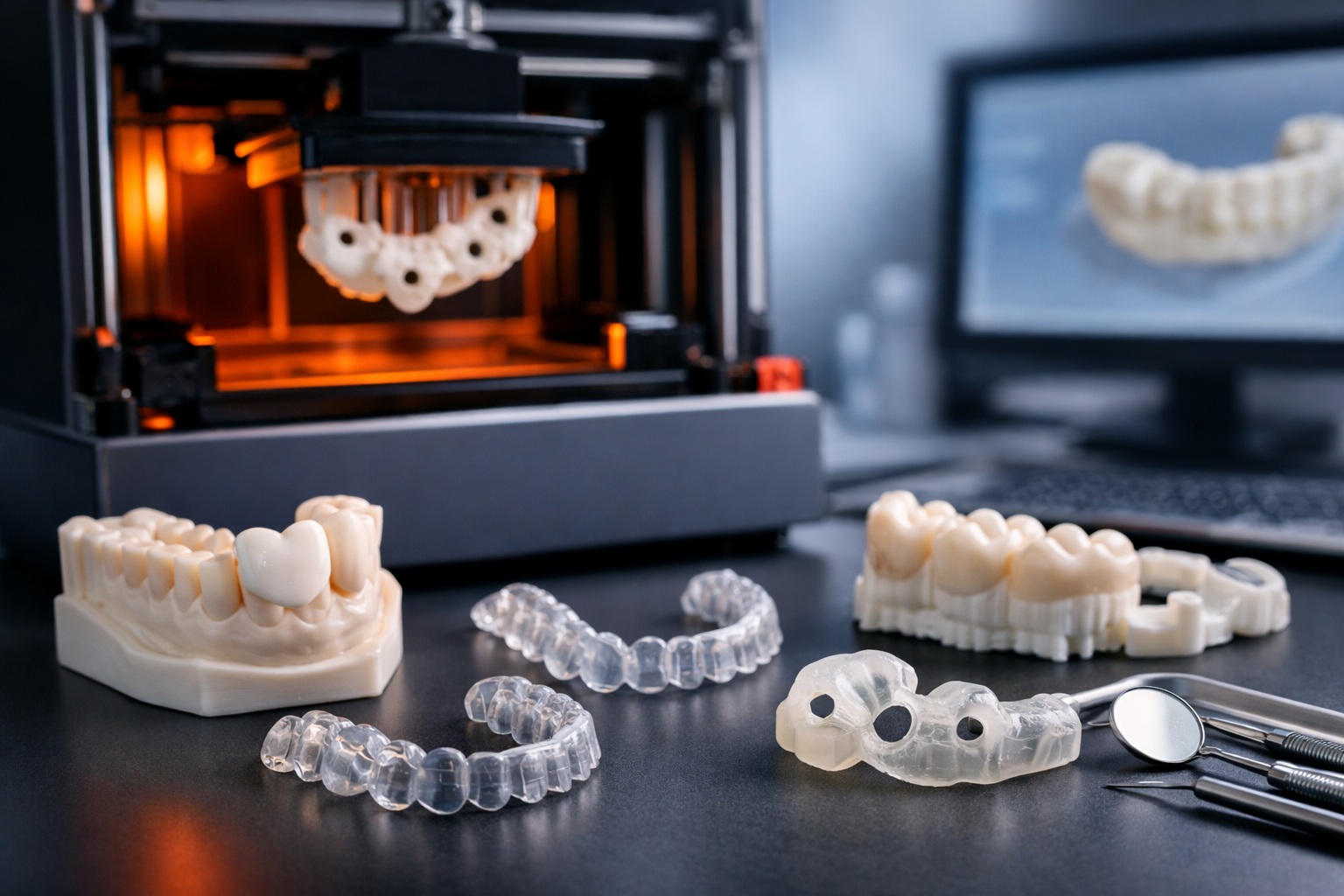
This article explores the key aspects of rapid prototyping, a crucial step in the product development process that offers significant benefits.
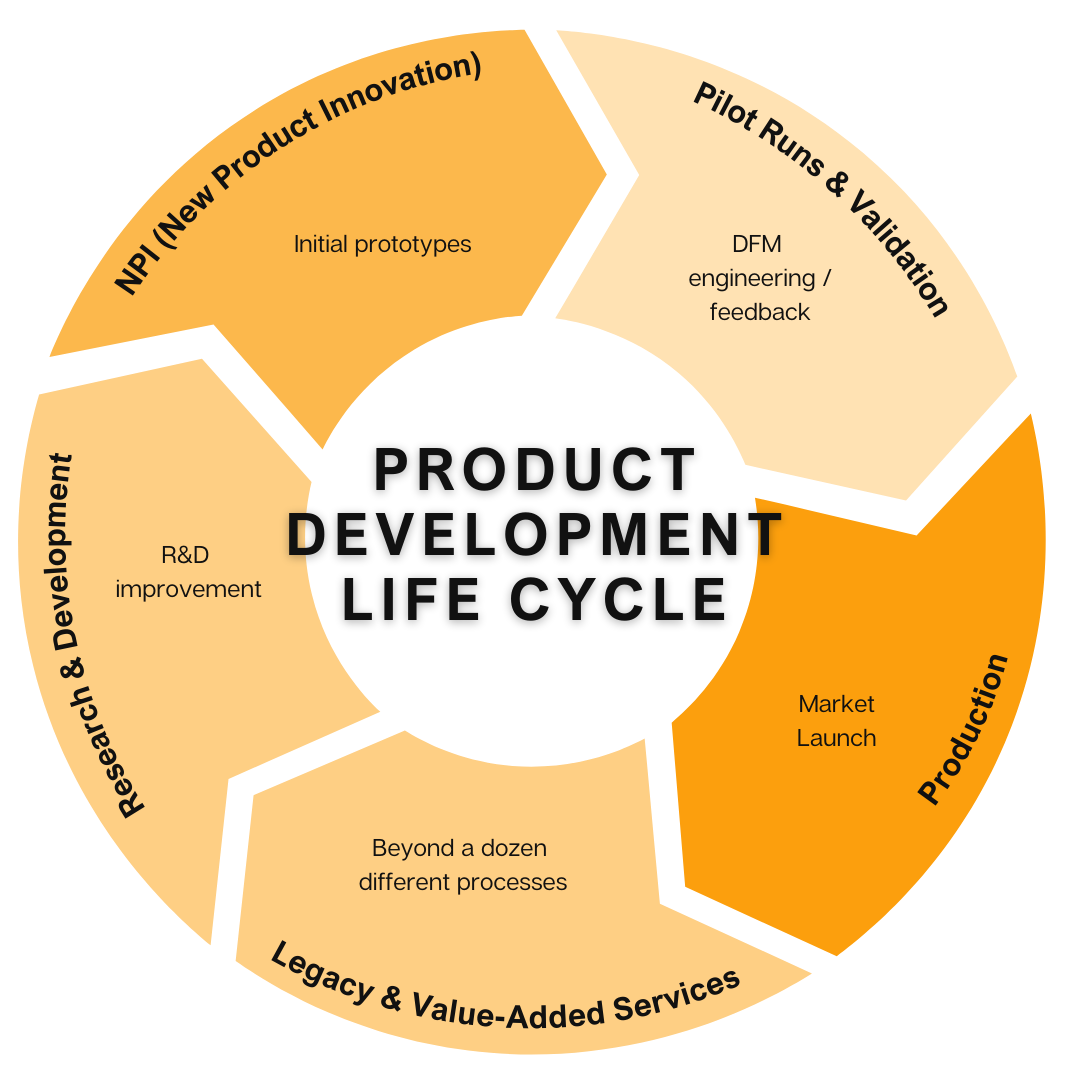
What is Rapid Prototyping?
Rapid prototyping is a game-changing method in manufacturing that enables the fast production of physical parts, models, or assemblies directly from 3D Computer-Aided Design (CAD). This cutting-edge process primarily uses additive manufacturing, widely recognized as 3D printing , to build prototypes layer by layer.
The core advantage of rapid prototyping is its ability to convert digital designs into physical prototypes quickly. These prototypes can vary in detail:
- High-fidelity prototypes closely replicate the final product, making them ideal for testing functionality and appearance.
- Low-fidelity prototypes are simpler and used for early-stage concept validation, helping teams assess basic design ideas before committing to costly production.
Although additive manufacturing is the most popular technique, rapid prototyping encompasses a variety of other manufacturing methods. Traditional approaches like high-speed machining, casting, molding, and extruding are also used, depending on the project’s needs.
Here’s a breakdown of these methods:
- Subtractive techniques: These involve cutting away material using tools like milling machines, grinders, or lathes to shape the prototype.
- Compressive techniques: These involve shaping materials by compressing semi-solid or liquid substances into molds before they solidify. Examples include casting and compressive sintering.
This broad range of methods highlights the versatility of rapid prototyping, making it adaptable to various designs and materials. Its flexibility allows manufacturers to experiment, refine, and perfect their products efficiently, saving both time and resources.
By combining speed, precision, and adaptability, rapid prototyping is transforming product development across industries—from automotive to healthcare—paving the way for faster innovation.
The Importance of Rapid Prototyping in Product Development
In today’s fast-paced market, staying competitive is essential. One powerful way to achieve this is by integrating rapid prototyping into your product development process. Rapid prototyping doesn’t just accelerate the design cycle—it also promotes a more flexible and agile development approach. By quickly producing prototypes at different stages, from initial concepts to visual models and fully functional versions, teams can spot and fix design flaws early. This proactive method reduces costly revisions later and streamlines the journey to creating a high-quality final product.
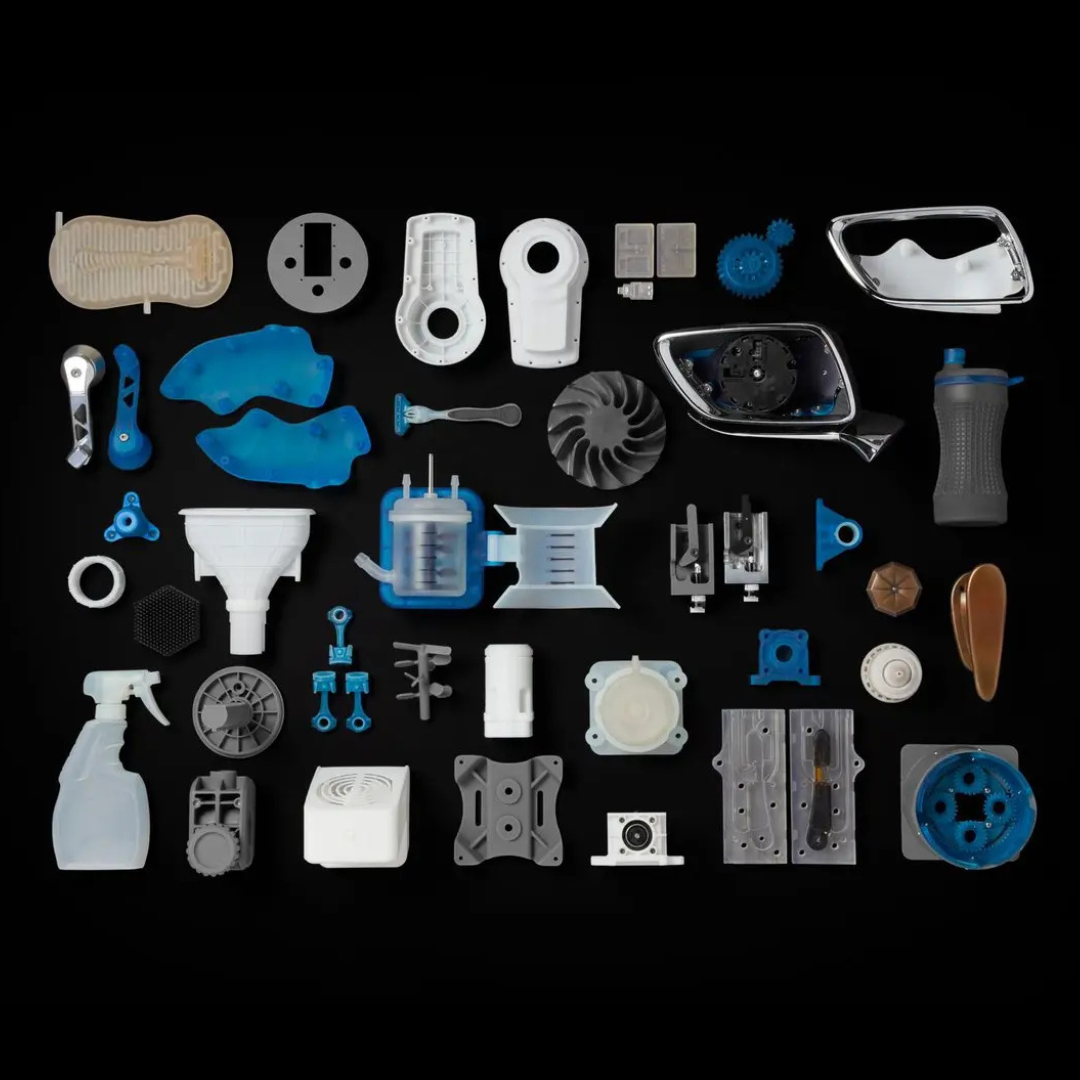

Benefits of Rapid Prototyping in Product Development
Accelerated Product Development
Rapid prototyping speeds up the iteration process, shortening development cycles and reducing time-to-market. In today’s competitive environment, this quick turnaround is critical for maintaining a competitive edge by swiftly moving from concept to product.
Cost Savings
By detecting design flaws and functional issues early, prototyping minimizes expensive revisions during later production phases. This early problem-solving reduces overall development costs.Enhanced Creativity
The iterative nature of rapid prototyping fosters experimentation and innovation. Designers can quickly test and refine concepts, leading to more innovative solutions and an adaptive product development process.Real-Time Feedback
Prototypes can be tested with actual users, providing immediate feedback. This direct user input allows for informed design adjustments, ensuring the final product aligns with user preferences and needs.Customization and Personalization
Rapid prototyping facilitates the development of tailored solutions, allowing companies to meet specific user requirements. This ability to create personalized products enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty.Risk Mitigation
Early testing and validation reduce the likelihood of product failure. By refining concepts at the initial stages, companies can ensure that the final product meets customer expectations and market demands, significantly lowering the risk of a misaligned or unsuccessful product launch.
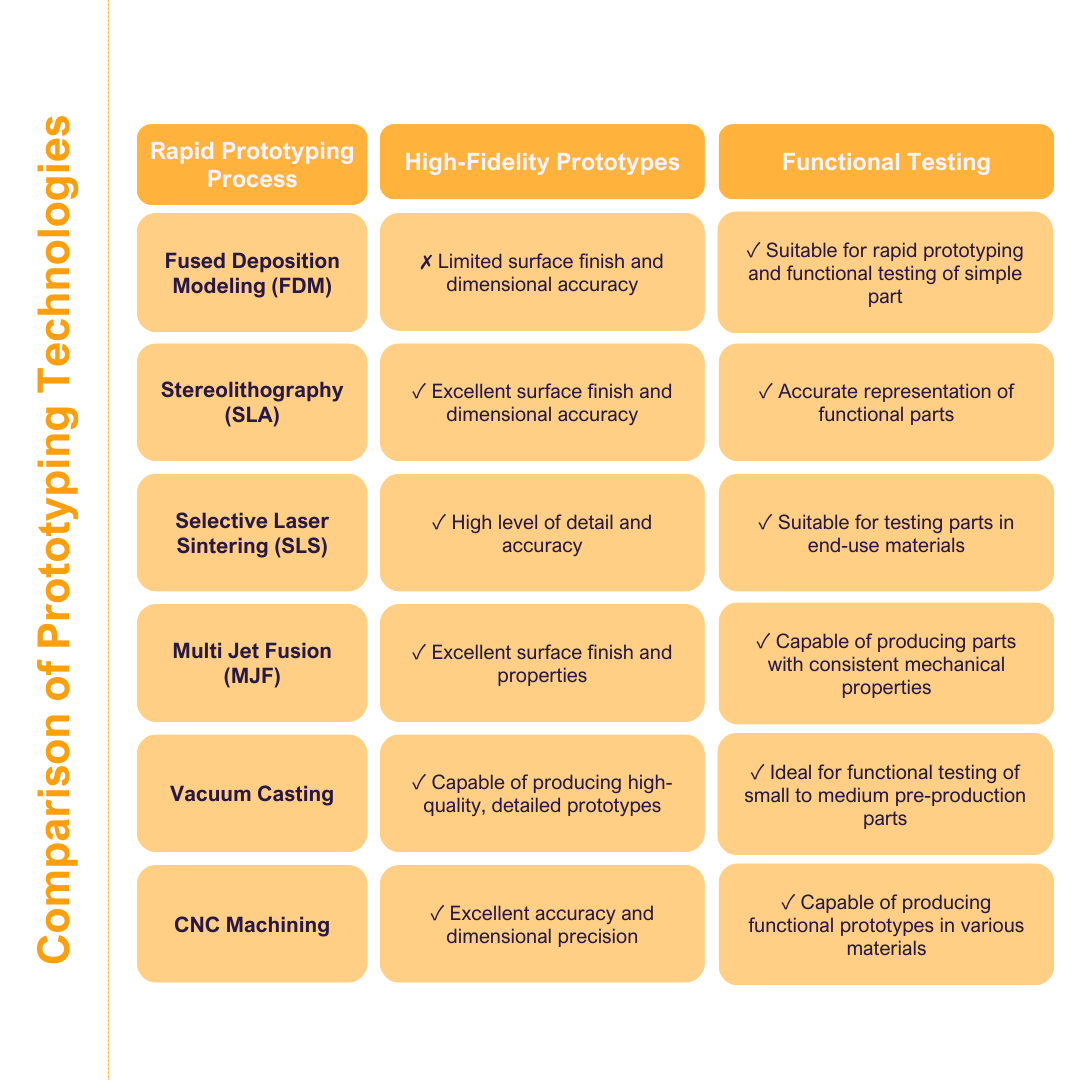
3D Printing FDM , 3D Printing service Singapore , 3D Printing service KL, 3D Printing SLA, 3D Scanning Malaysia
Low-Fidelity vs. High-Fidelity Prototypes: How to Choose the Right Approach
When developing a product, it’s important to choose the right type of prototype for your design stage. Let’s break down the two main types: low-fidelity and high-fidelity prototypes.
What Are Low-Fidelity Prototypes?
Low-fidelity prototypes are simple, early-stage representations of a product concept. They are often quick and inexpensive to create, using basic materials like paper sketches, wireframes, or cardboard models. These prototypes focus on testing broad ideas rather than specific details, making them perfect for gathering initial user feedback and refining the overall vision of a product. Their goal is to validate core concepts, allowing teams to quickly identify potential issues and make changes before investing too much time or money.
What Are High-Fidelity Prototypes?
High-fidelity prototypes are more advanced and closely resemble the final product in terms of design, functionality, and user experience. They often include detailed visuals, interactive features, and realistic user interfaces. Because of their polished nature, high-fidelity prototypes are used for more in-depth testing, including usability studies and stakeholder presentations. These prototypes allow teams to identify and address specific design flaws and functionality issues before full-scale production.
When to Use Each Prototype
- Low-Fidelity Prototypes are ideal in the early stages of design, where quick iterations and broad feedback are essential. They’re best for brainstorming sessions, early user testing, and concept validation.
- High-Fidelity Prototypes are most useful in the later stages, where precise details and a near-final user experience are needed. They help stakeholders visualize the product and enable teams to refine the design based on detailed user feedback.
By choosing the right prototype at the right stage, you can streamline your design process, improve collaboration, and create a product that meets both user needs and business goals.
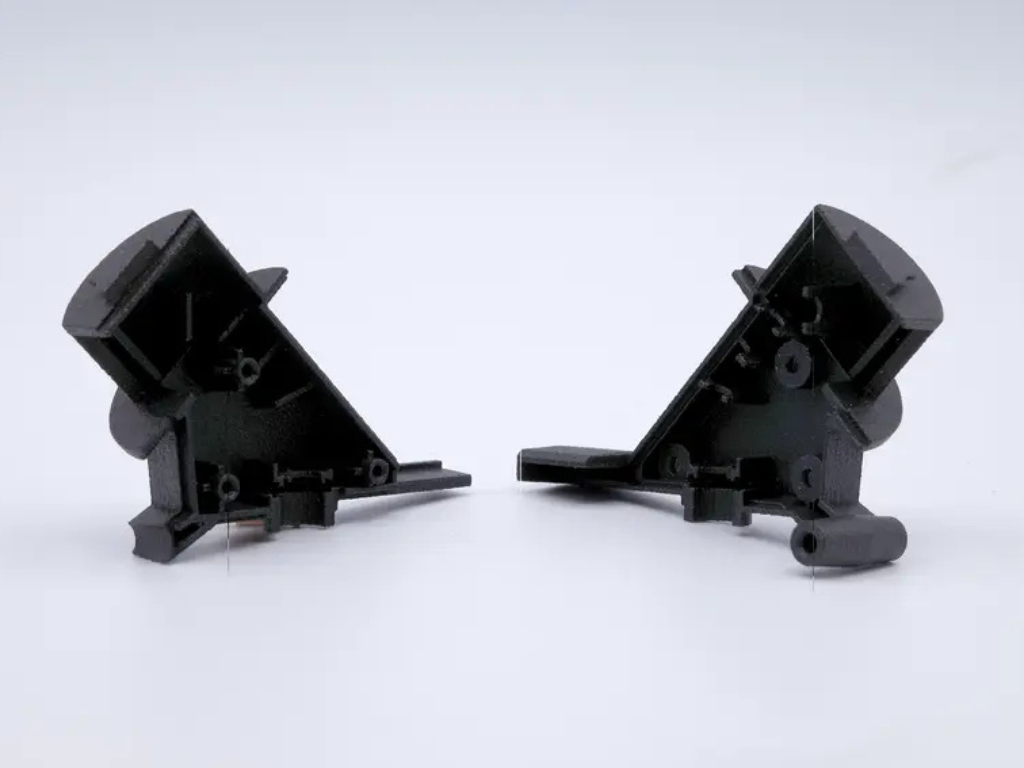

Collaborate with 3D printing bureau to choose the best material and optimize build orientation for your project’s needs.Explore our 3D Printing Materials Guide to learn about various plastic and metal materials across technologies.
Discover more at projet.my. For assistance, reach out to our applications engineer at enquiry@projettech.com or +604-2858 335.