Did You Know ? ?
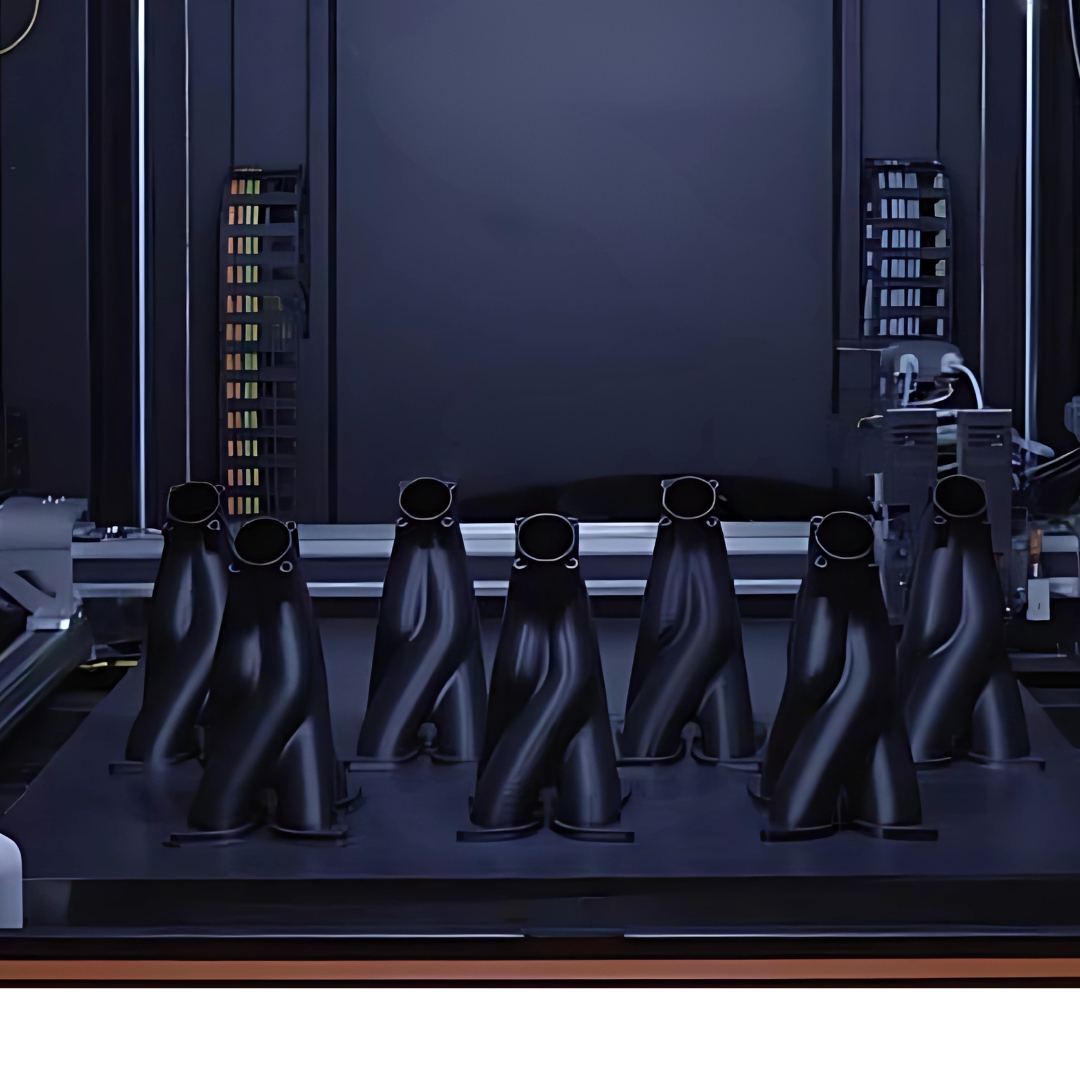
You can achieve low-volume production with injection-molding quality using Additive Manufacturing (AM). Whether you’re in automotive, medical, or consumer goods, AM can bridge the gap between prototyping and mass production.
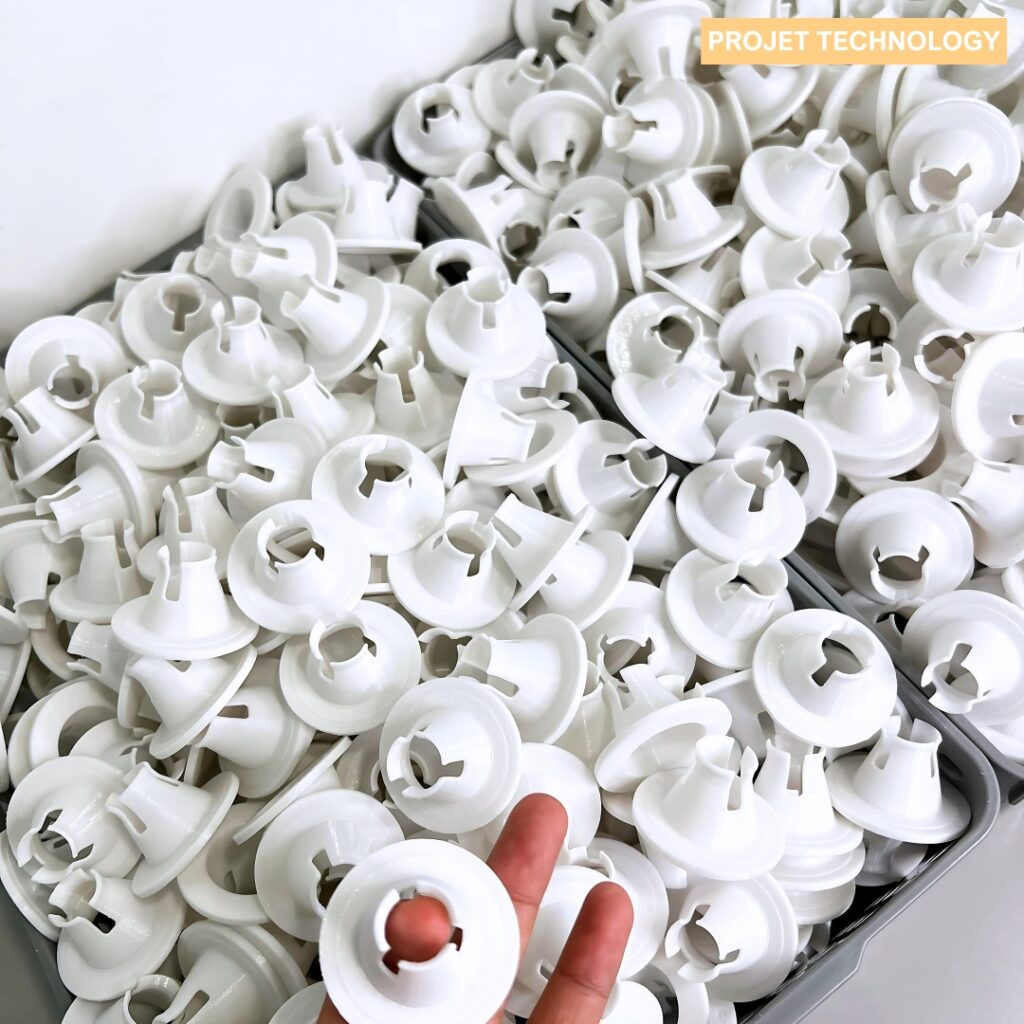

Benefits of AM for Small-Batch Production
For low volume production, additive manufacturing offers a cost-effective solution, addressing some of the limitations of traditional manufacturing:
- Avoid the high costs and long lead times associated with tooling.
- Print on demand, supporting small volume manufacturing.
- Create complex designs in a single print, reducing assembly time.
- Bring production in-house, mitigating supply chain disruptions.
Low Volume Production is the Future of Manufacturing
Low volume manufacturing offers a flexible and cost-effective alternative to the high-volume model. However, traditional methods can come with high setup and tooling costs, and manufacturers are looking for more economically viable options for short production runs.
Think 3D printing can’t achieve high accuracy? You haven’t met Projet.
3D printing in manufacturing has come a long way, with many technologies now capable of meeting average production standards for accuracy, tolerance and surface finish.
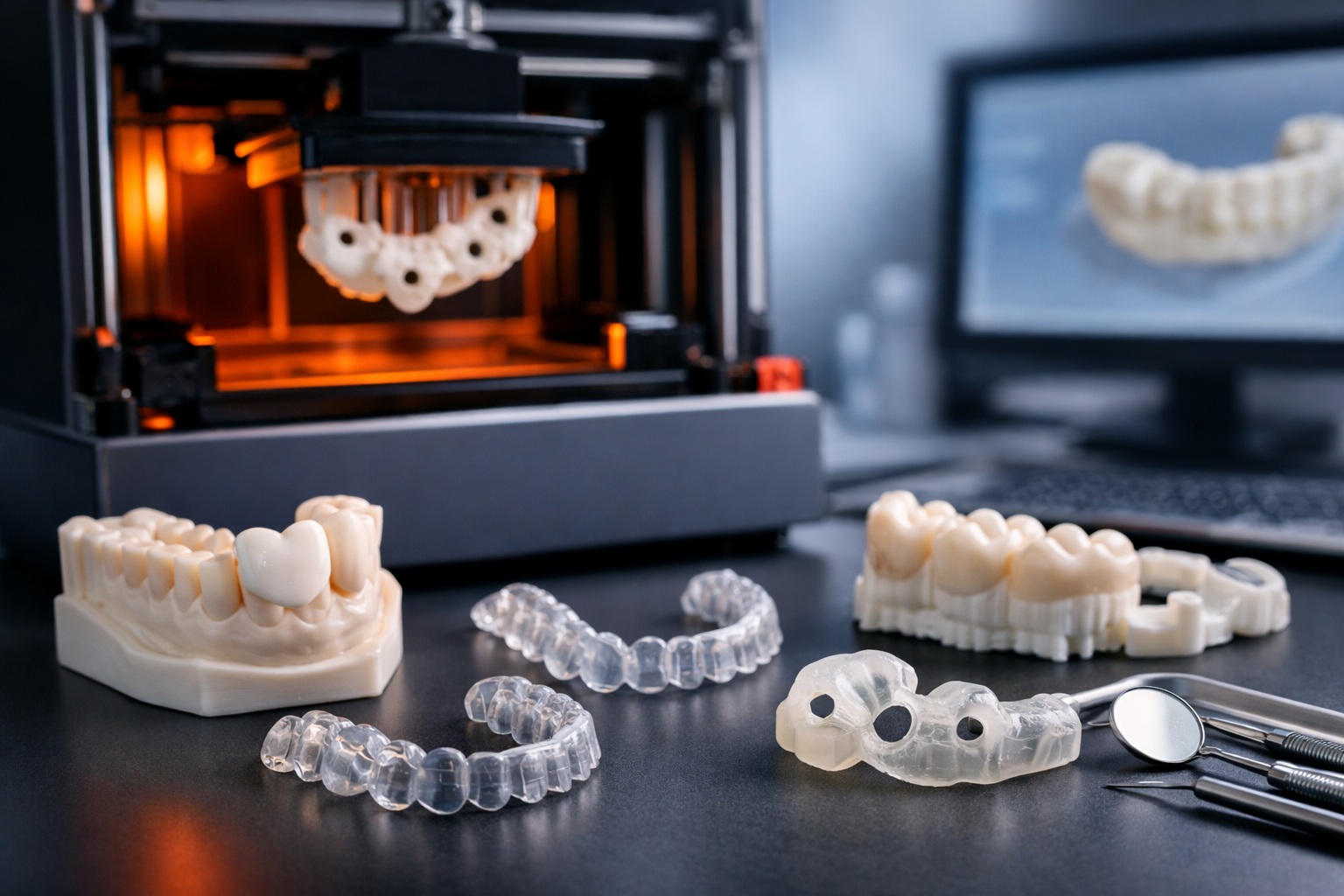
Low-volume production utilizing injection-molding quality achieved through Additive Manufacturing (AM) involves using AM to create injection molds for producing parts in small batches, often fewer than 10,000 parts, with the aim of matching or surpassing the precision and efficiency of traditional injection molding. This approach is particularly effective for prototyping, small-batch production, and custom part manufacturing, offering cost savings and faster lead times compared to traditional mold making.
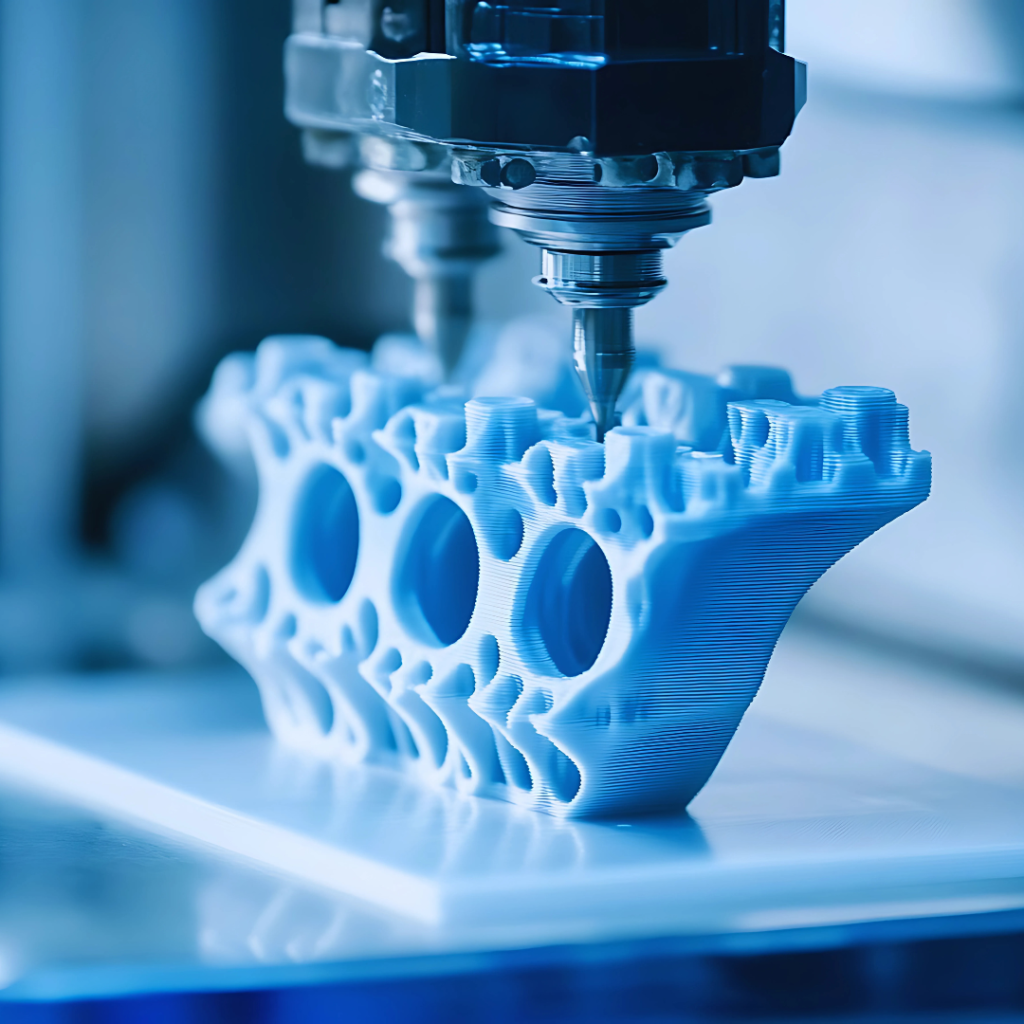

What is Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)?
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), also called Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF), is the most popular type of 3D printing. It works by melting plastic and stacking it layer by layer to build an object. Each layer is added one after another until the object is finished. FDM are great for making simple prototypes or basic models quickly and cheaply, especially for parts that would normally be made by machining. However, FDM isn’t as precise or detailed as other 3D printing methods like SLA or SLS, so it’s not the best choice for complex or highly detailed designs.
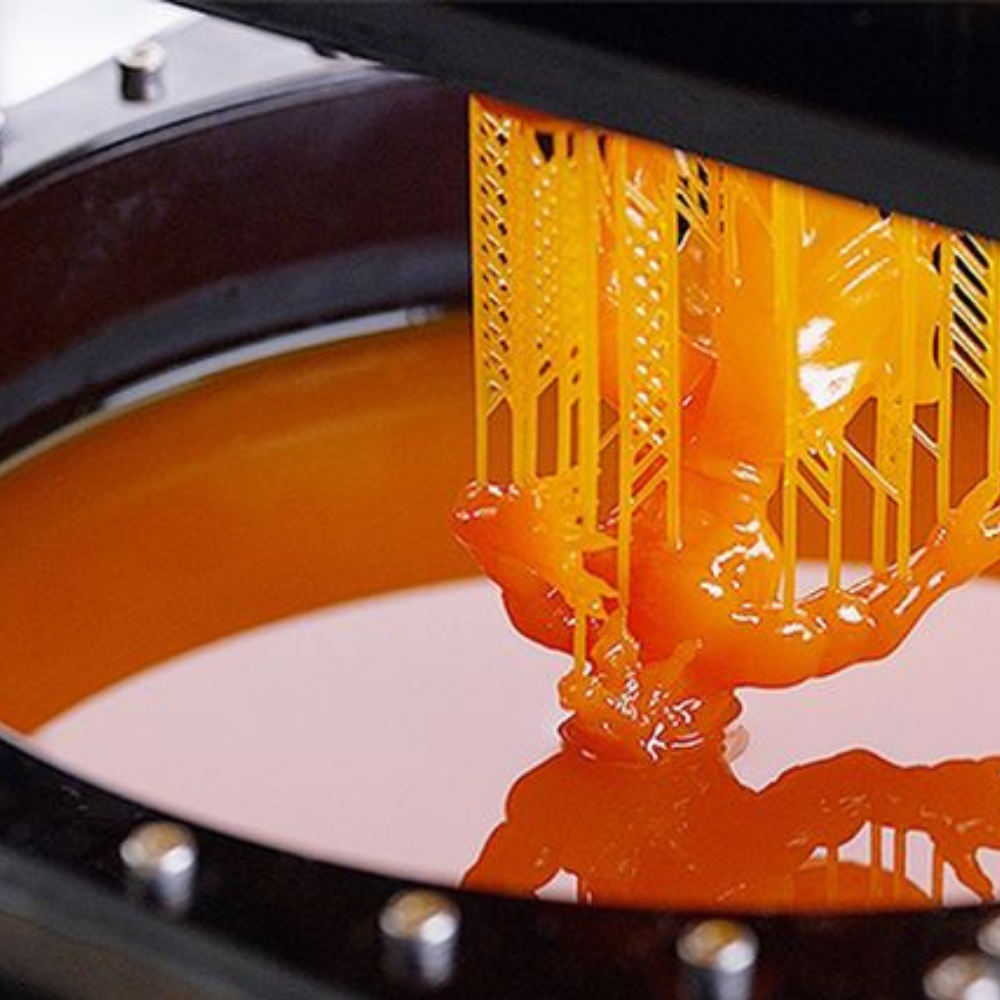

What is Stereolithography (SLA)?
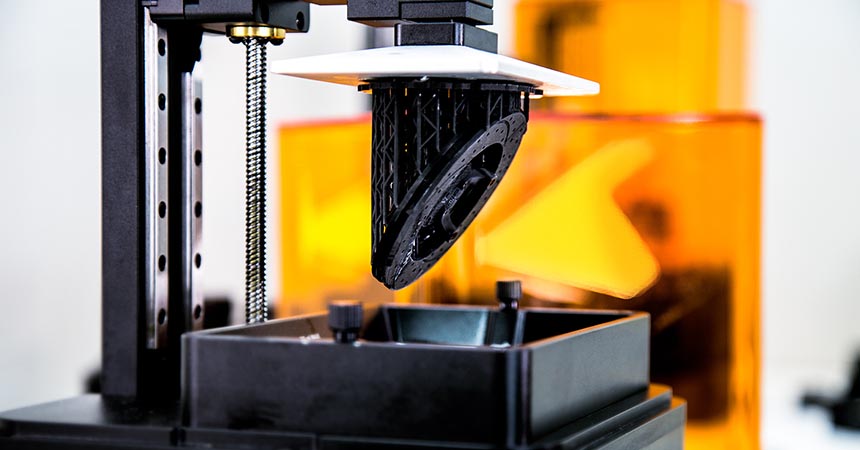
Stereolithography (SLA) 3D printing is the most common resin 3D printing process and has become vastly popular for its ability to produce high-accuracy, isotropic, and watertight prototypes and end-use parts.
SLA 3D printers produce parts with a range of advanced material properties, superior surface finishes, and fine features.
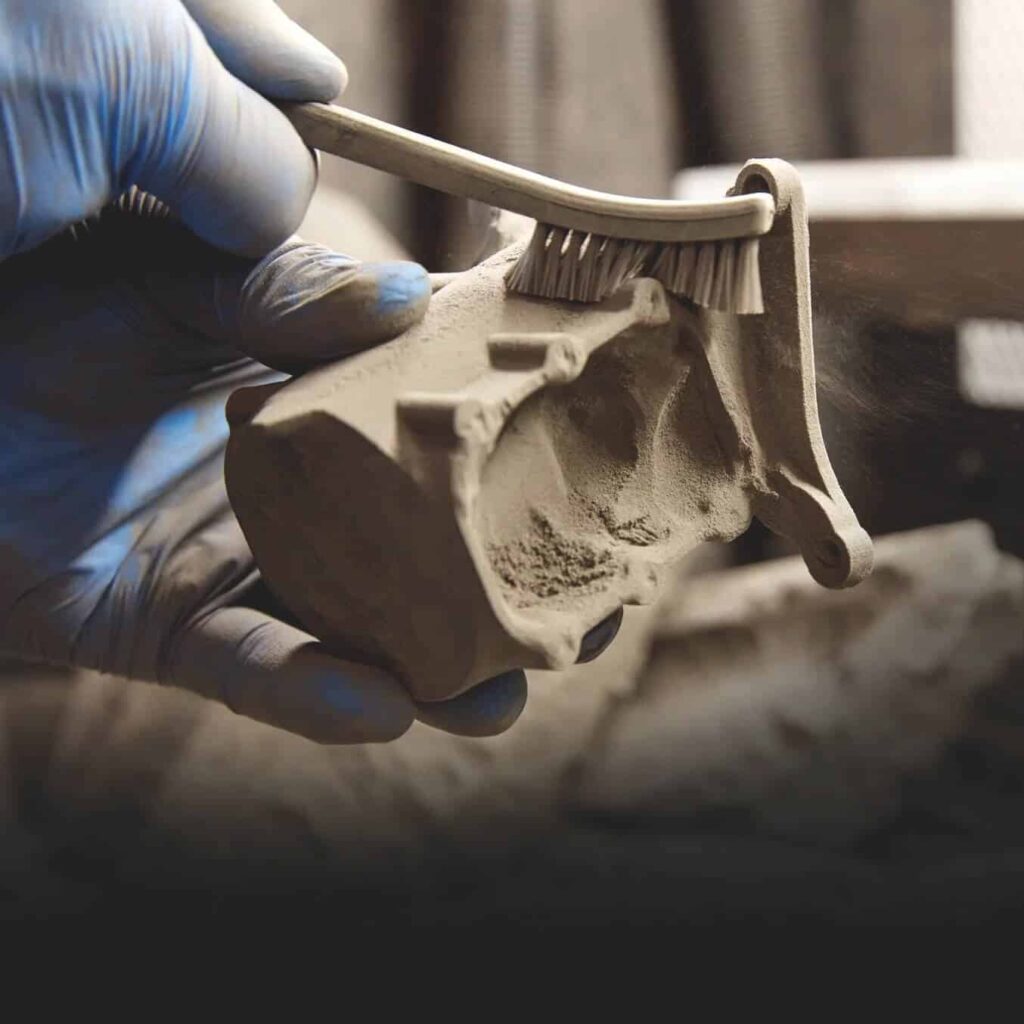

What is Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)?
Selective laser sintering (SLS) is a 3d printing process (additive manufacturing) that uses high-powered lasers to sinter, or bind, finely powdered material together into a solid structure. In this process, a printer lays down an even layer of powder and then precisely sinters that layer, repeating the deposition and sintering process until the part is complete.
SLS 3D printing is trusted by engineers and manufacturers across different industries for its ability to produce strong, functional part.
Ready to take your projects to the next level? Visit projet.my to learn more about our 3D printing services and explore the potential of additive manufacturing. For personalized assistance, reach out to our applications engineer at enquiry@projettech.com. We’re here to help you every step of the way.
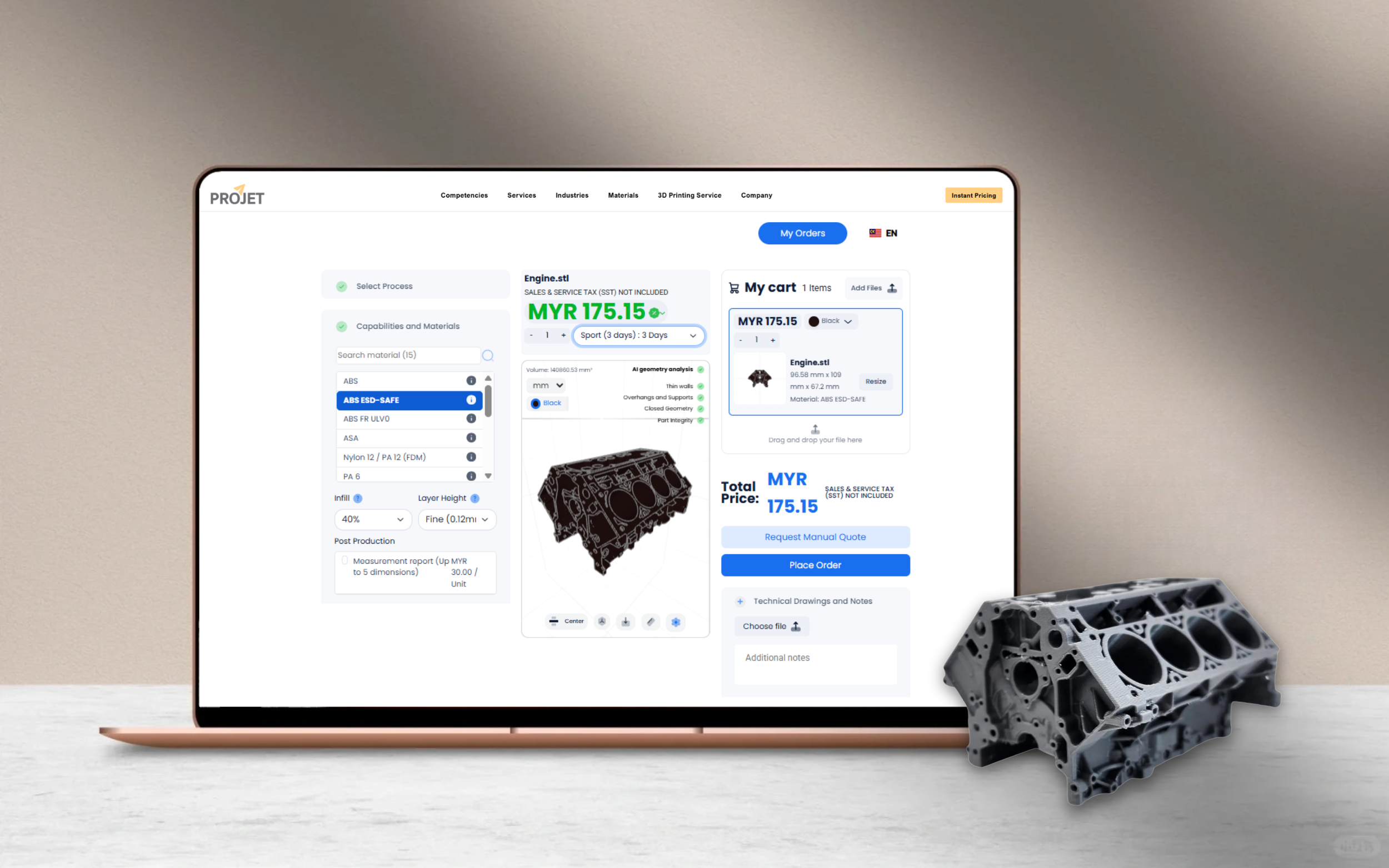
Don’t wait—unlock the power of 3D printing with Projet. Try our Online Instant Quote today and see how easy it is to bring your ideas to life!
3D Printing Service Malaysia , 3D Printing service Singapore , 3D Printing service KL , 3D Printing service Selangor, 3D Scanning Malaysia
3D Printing Services
Instant Price