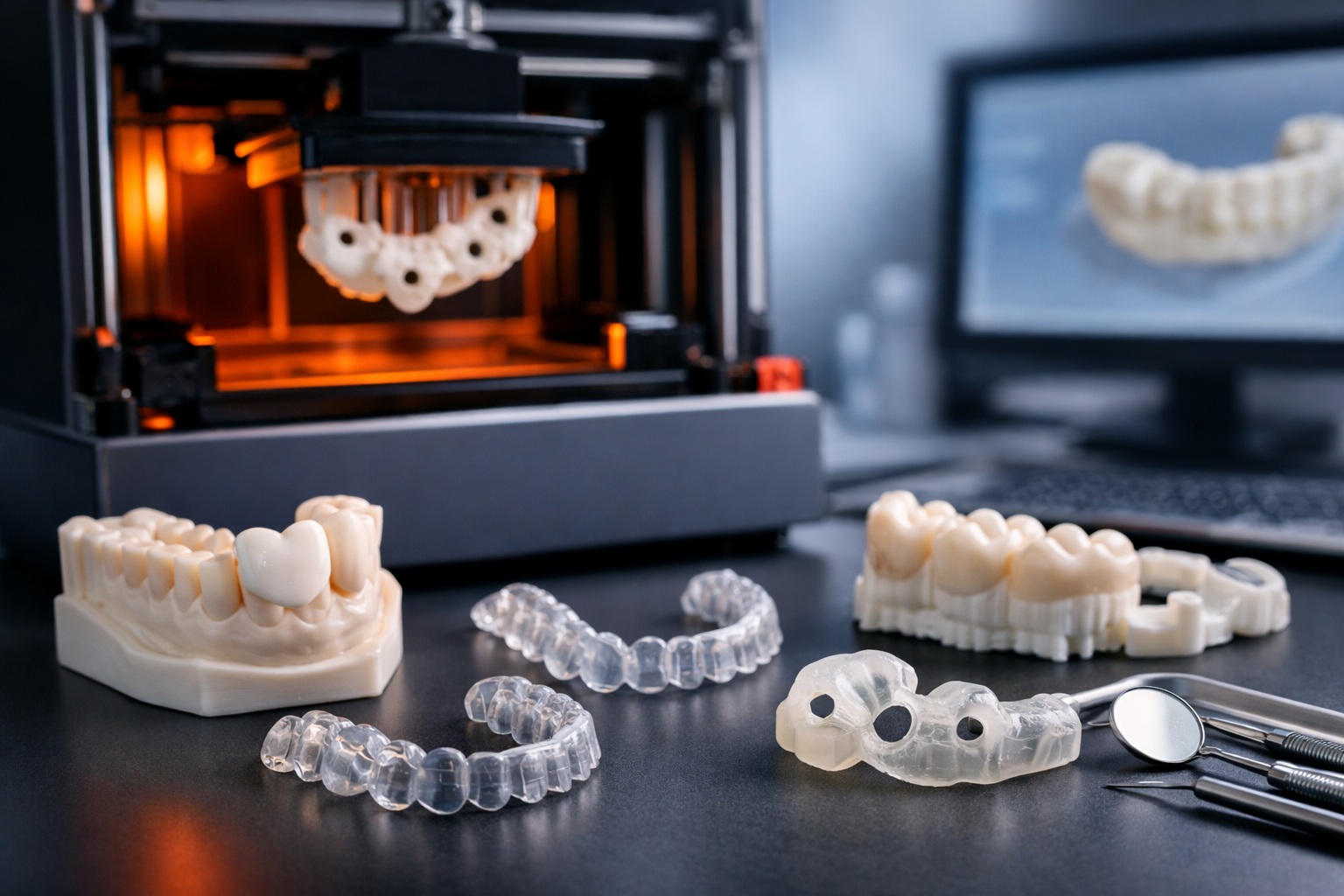
3D Printing, also known as Additive Manufacturing, creates three-dimensional objects from digital CAD files by successively laying down thin layers of material until the product is complete. It has higher initial setup costs than traditional processes, but the technology is evolving and continually becoming cheaper.
Since its introduction in the 1980s, 3D printing has evolved remarkably, offering companies across various industries enhanced flexibility to turn ideas into reality. Innovations like high-performance materials and projection printing have greatly expanded 3D printing’s benefits.
Will 3D printing replace traditional manufacturing? Not anytime soon. However, 3D printing offers significant advantages, making it ideal for various prototyping and industrial applications. The additive manufacturing process enhances flexibility, reduces waste, and speeds up production.
Most Popular 3D Printing Processes
- Stereolithography (SLA)
SLA technology enables the production of high-precision prototypes and parts with exceptionally smooth surfaces. Its ability to create intricate details makes it an ideal choice for manufacturing complex components, such as sensor housings and aerodynamic part prototypes. - Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
This technology leverages laser-based techniques to melt and solidify thermoplastic powders, making it highly effective for producing components from polyamide and other thermoplastic materials. This approach offers significant advantages, particularly in the manufacturing of complex, high-quality parts. - Selective Laser Metal (SLM)
SLM is a crucial technology for producing complex, high-performance metal parts. By selectively melting successive layers of powder through the precise interaction of a laser beam, SLM enables the creation of strong, lightweight components that are ideal for aerospace applications. This advanced technique is essential for manufacturing engine components, structural support systems, and other critical parts that ensure aircraft safety and optimal performance. - Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is an extrusion-based 3D printing technology that uses thermoplastic polymers in filament form as its build materials. This method is widely recognized for its versatility, affordability, and broad range of applications.
Advantages Of 3D Printing Over Traditional Manufacturing

Production Time:
When comparing 3D printing to traditional manufacturing, production time is a key factor. Conventional methods, like injection molding, often take 1-2 months for mold creation, resulting in high costs for small batches. Conversely, 3D printing eliminates tooling, enabling instant production and faster time-to-market, providing a competitive edge.
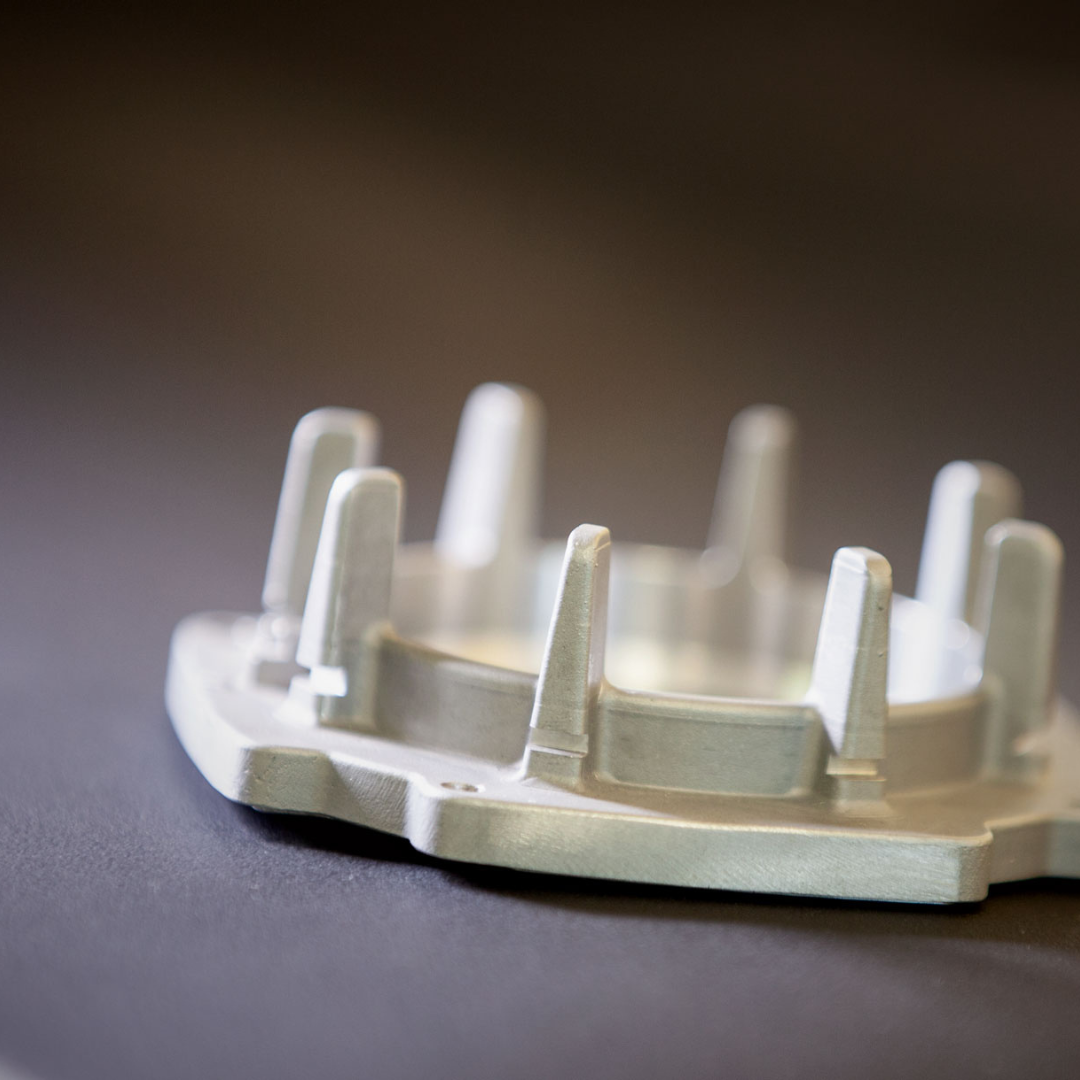
Cost:
3D printing offers cost efficiency by maintaining consistent per-unit costs regardless of quantity, from one to hundreds of parts. Unlike traditional manufacturing, which demands costly tooling for mass production, 3D printing is ideal for short runs, slashing production costs and minimizing setup, labor, and assembly time.
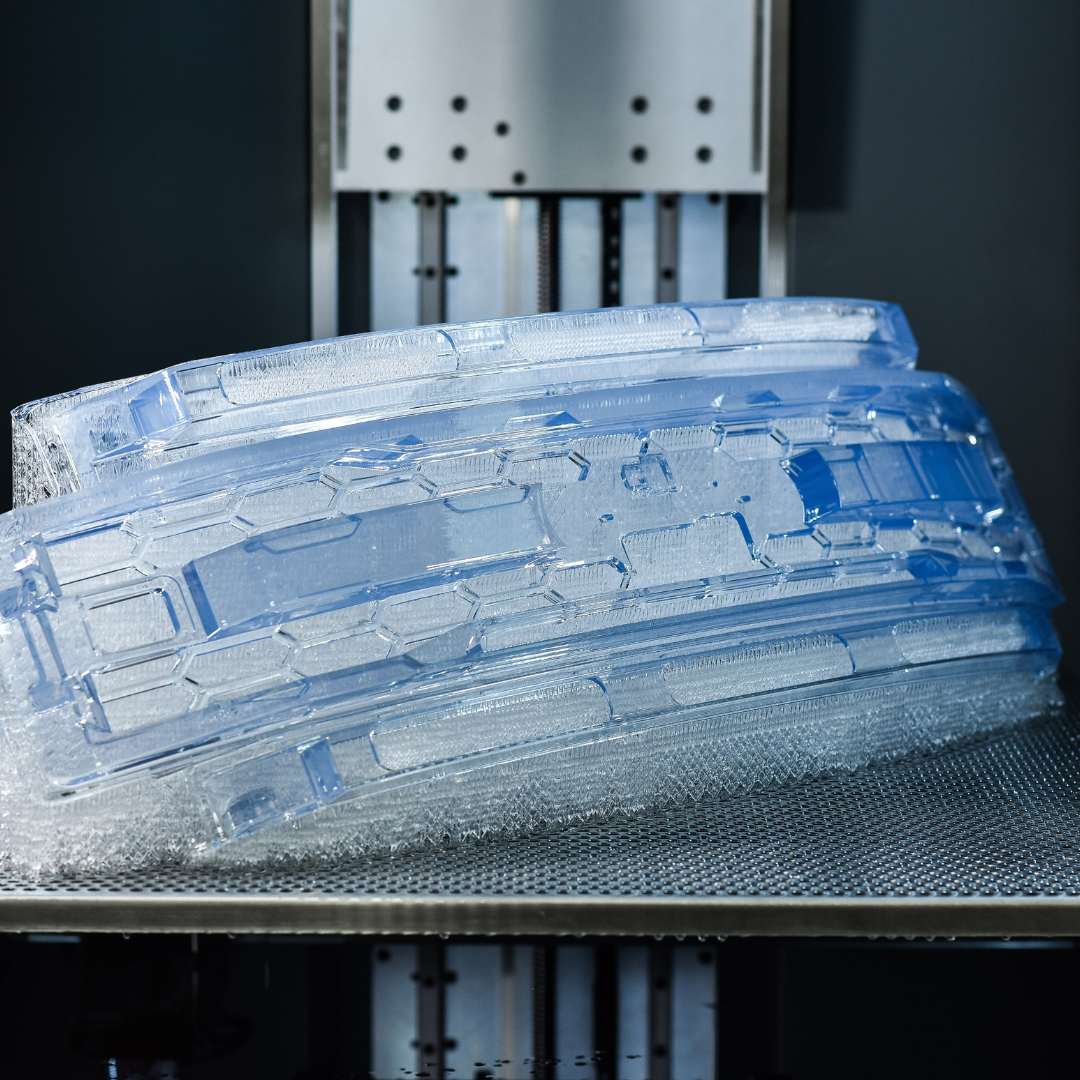

Complexity:
Traditional manufacturing can be costly due to complex designs requiring precise expertise. In contrast, 3D printing addresses these challenges by offering consistent pricing regardless of complexity. It also consolidates parts, reducing assembly time and boosting efficiency, which provides a competitive edge.
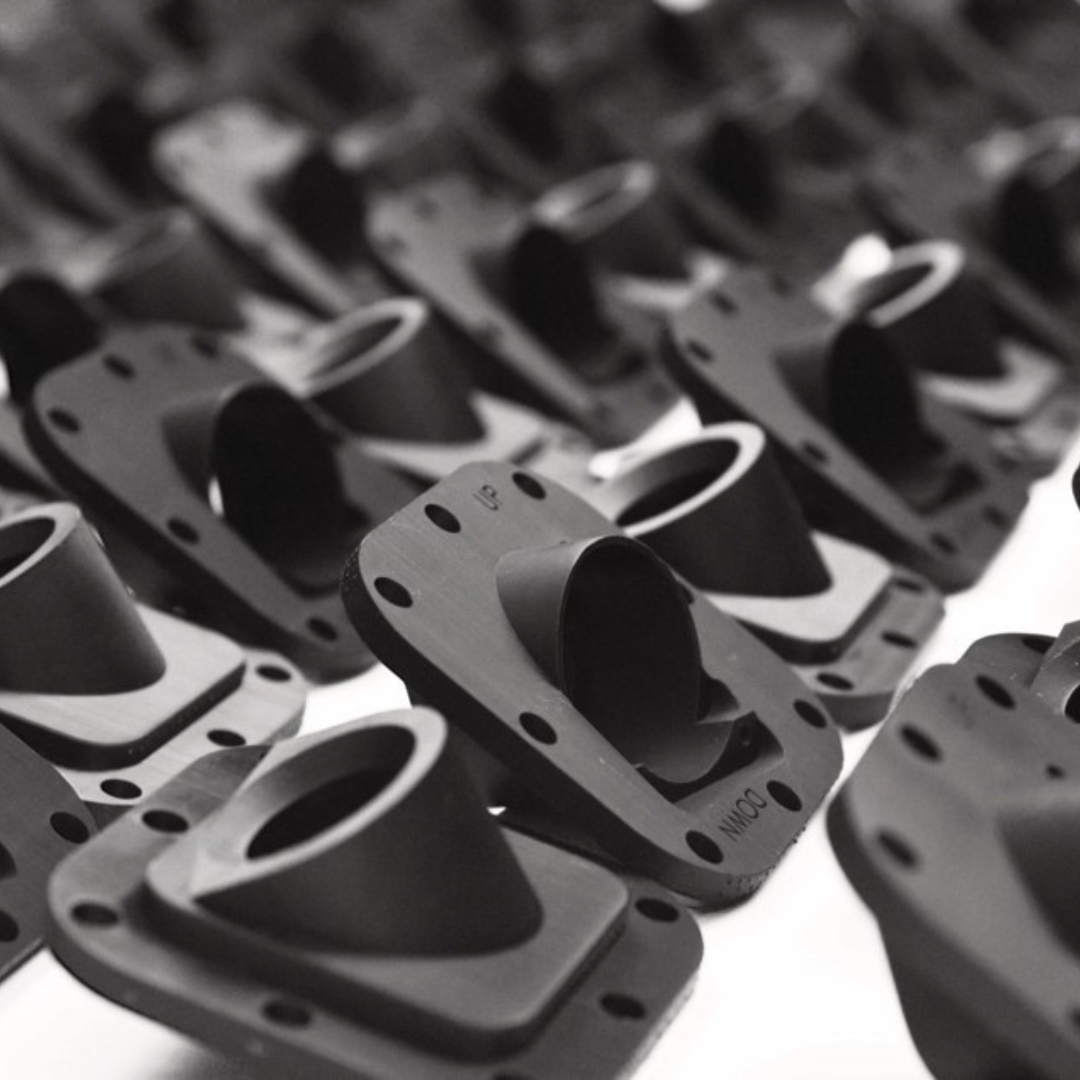

Manufacturing Speed:
3D printing revolutionizes product development by swiftly turning ideas into prototypes and final products, far outpacing traditional methods. It seamlessly combines multiple parts into one piece, removing the assembly stage and drastically cutting manufacturing time, thus boosting efficiency.
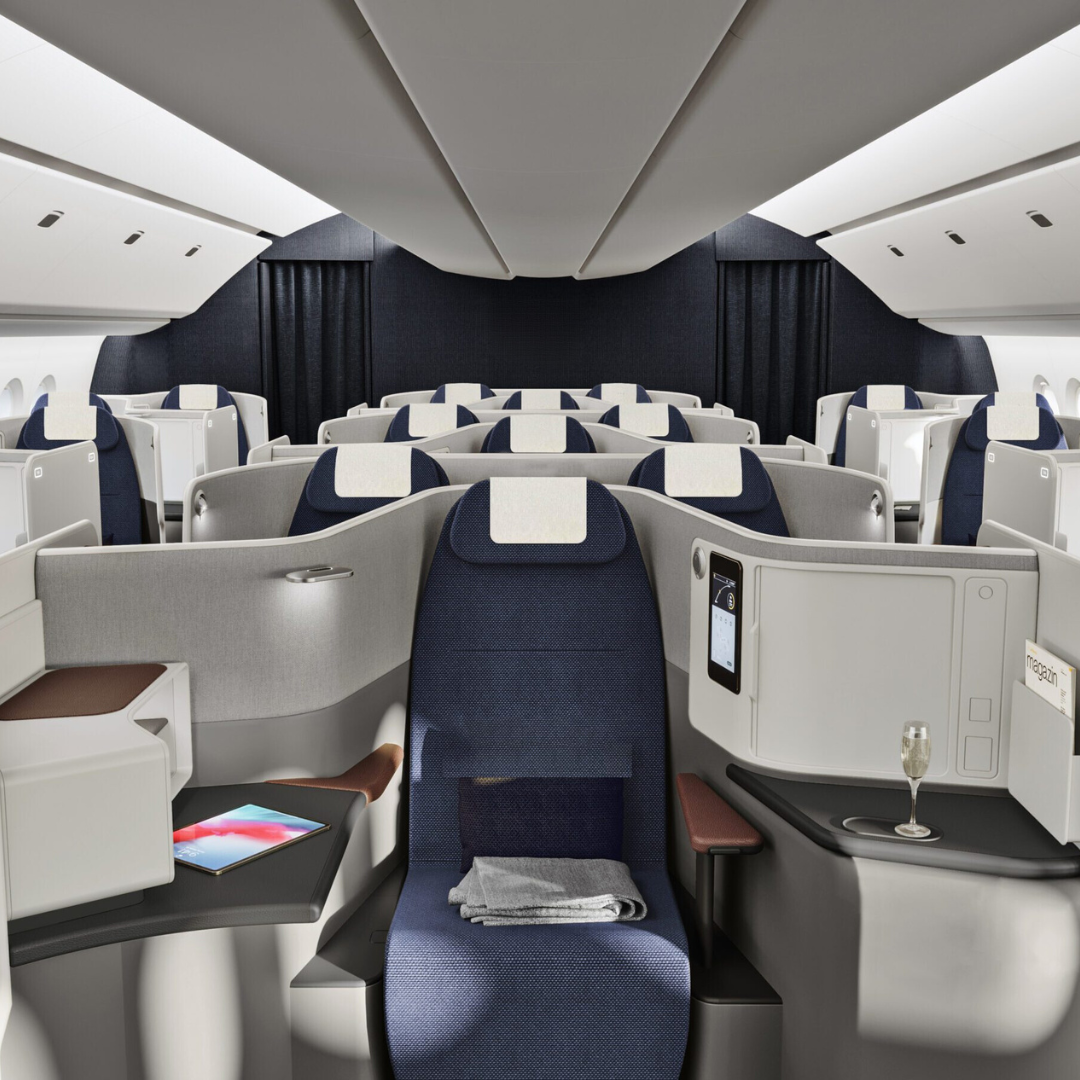

Interior Components:
Aircraft interior components range from avionics equipment to cabin accessories like galley inserts and light fixtures. Popular 3D printing methods such as SLA (stereolithography) and SLS (selective laser sintering) are widely used to fabricate these essential parts, offering precision and efficiency in aerospace manufacturing..

Warehousing:
Traditional manufacturing typically requires mass production and extensive warehousing, increasing storage, land, and labor costs, which compresses profit margins. In contrast, 3D printing supports on-demand, low-volume production, cutting warehousing needs and costs. Embrace 3D printing to enhance capital efficiency and boost profitability.
Connect with Projet:
If you’ve had a positive experience with Projet that you’d like to share, please reach out to us at enquiry@projettech.com. We eagerly anticipate hearing from you.
For additional information, visit our website for comprehensive details about our services and contact information. Our friendly team is ready to assist you at any time.