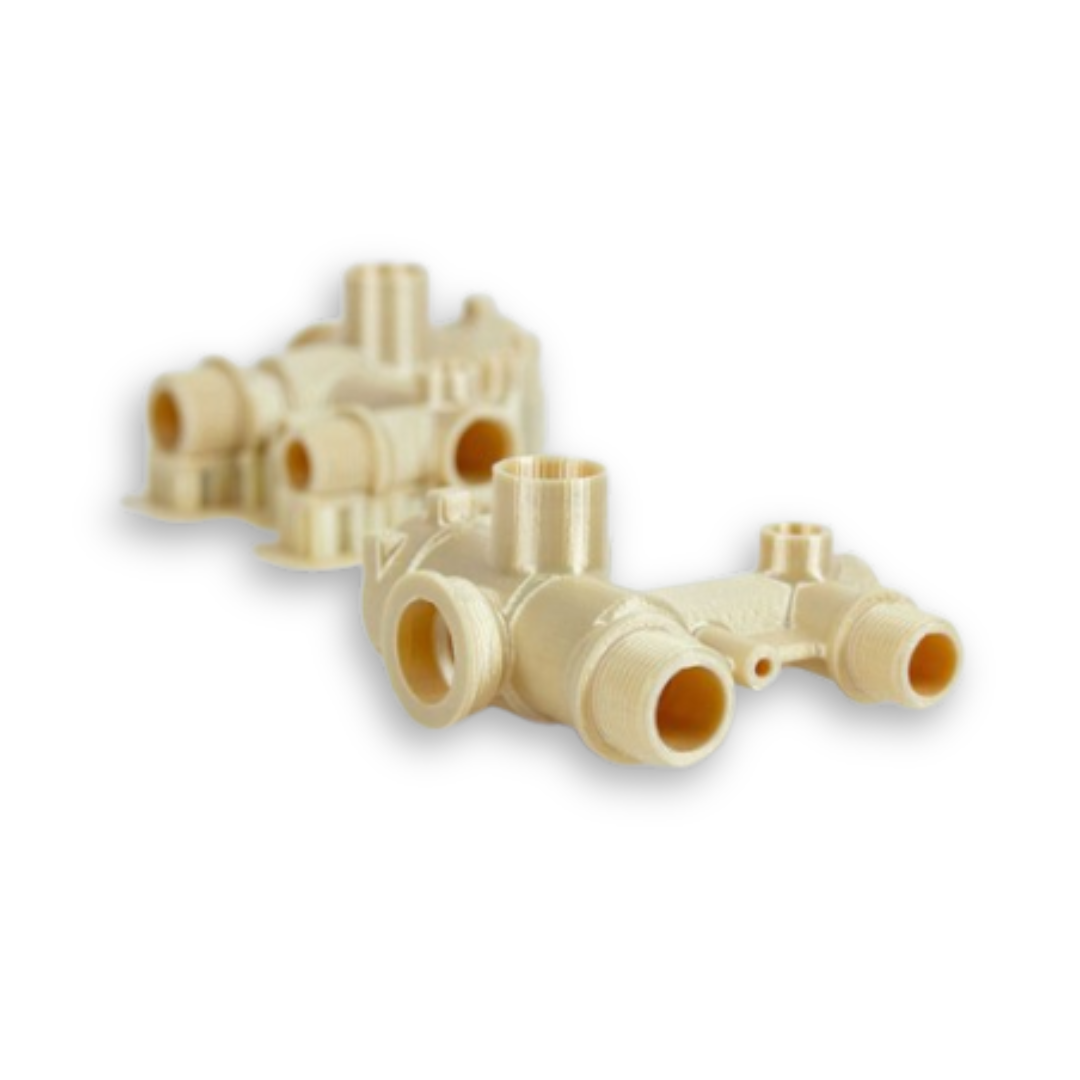
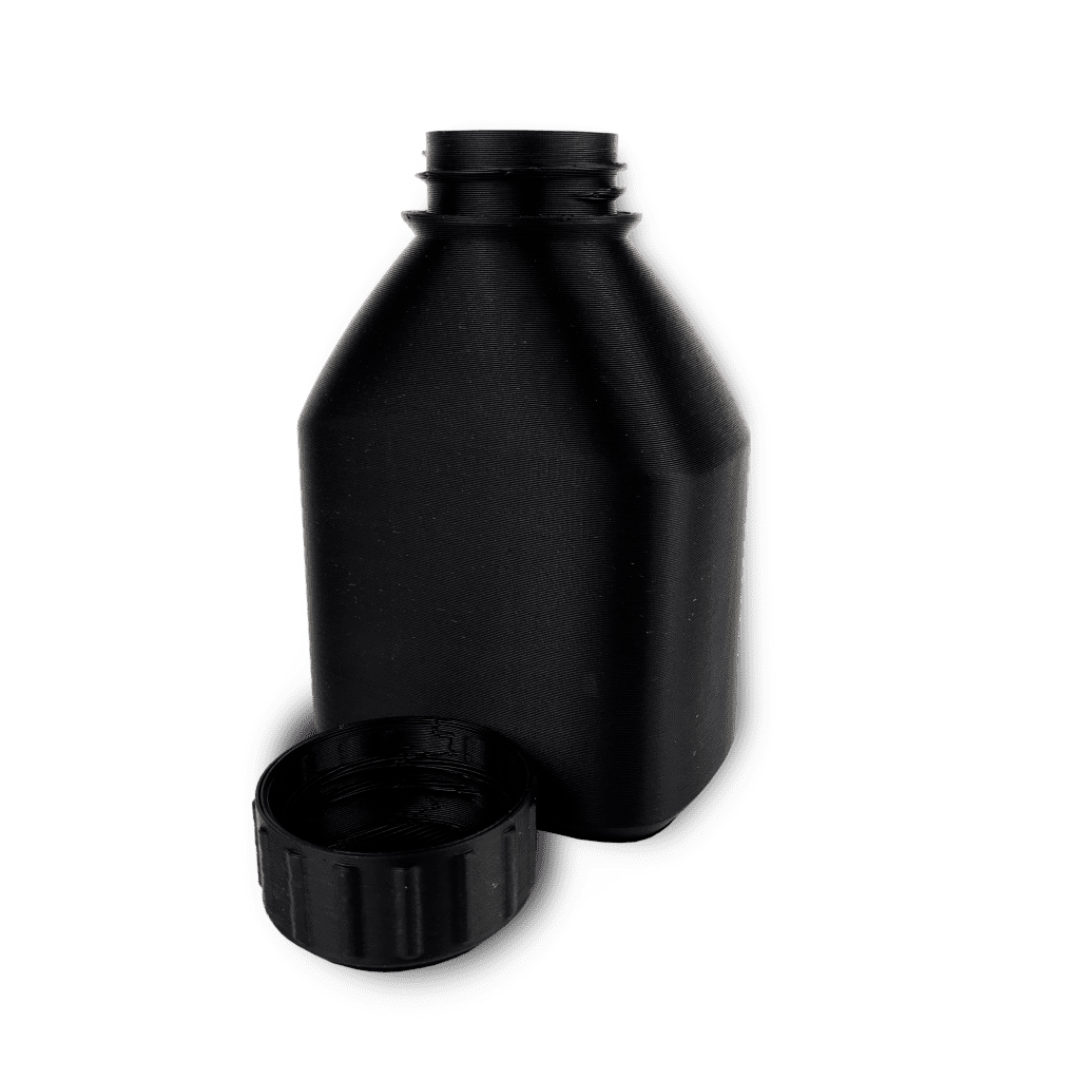
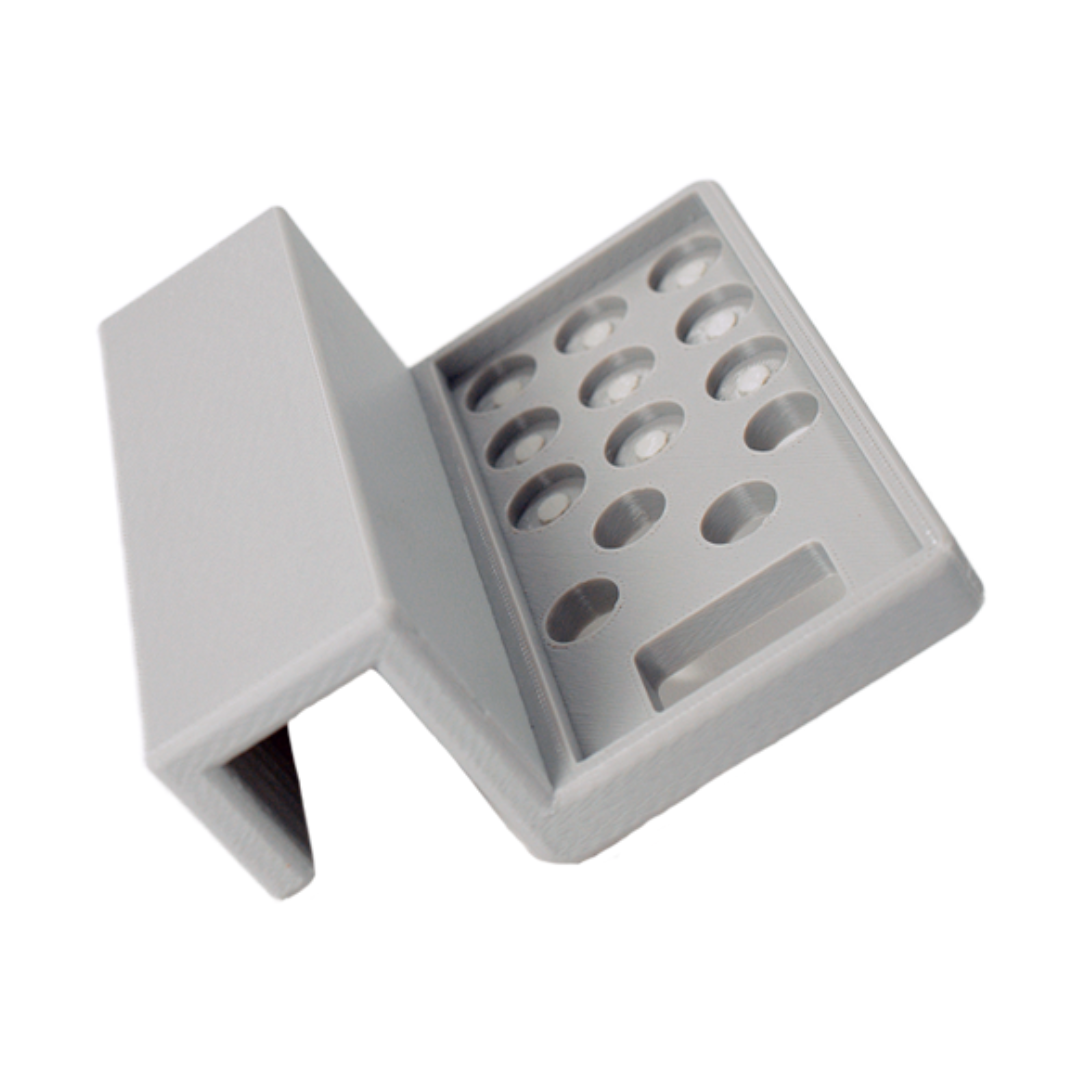
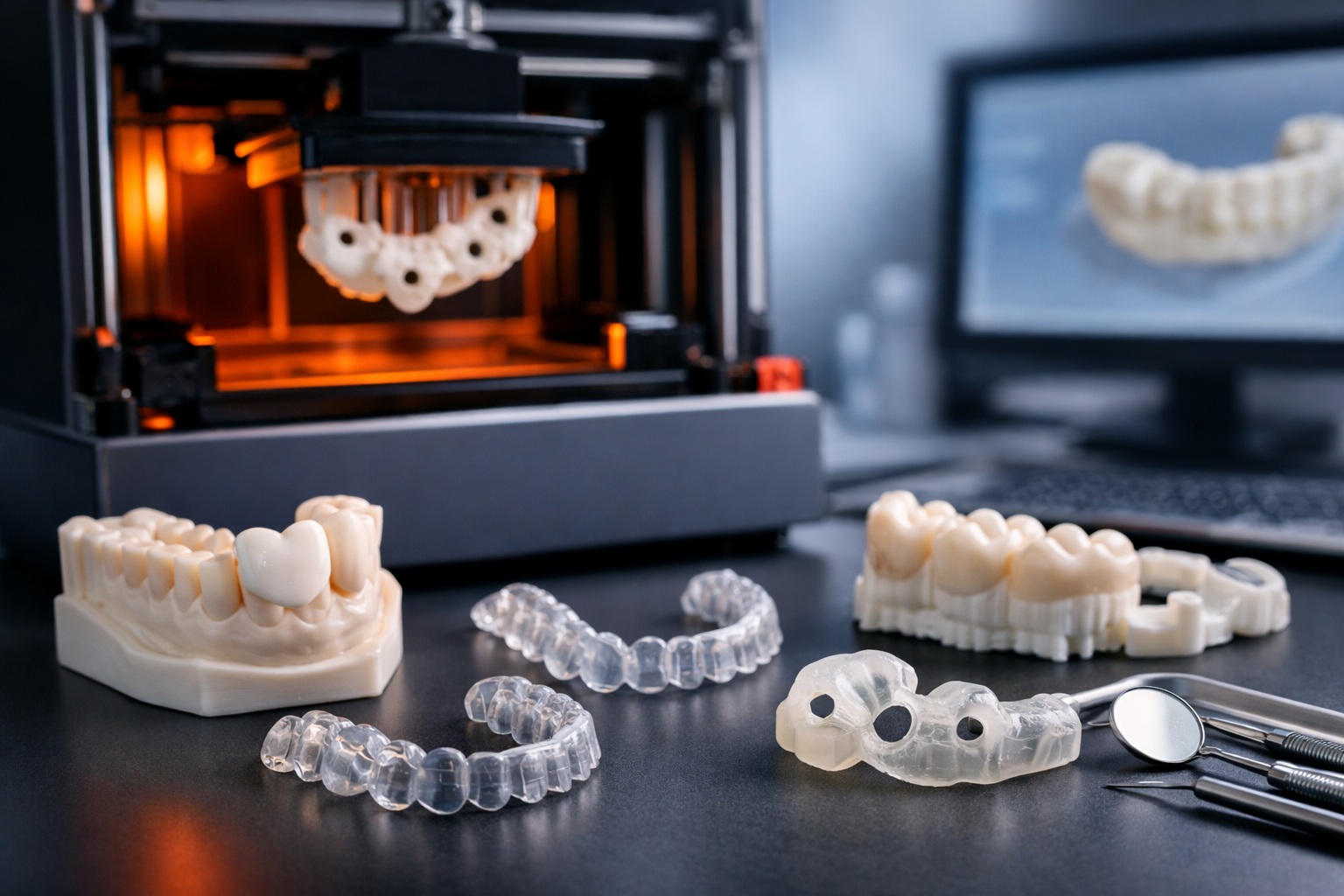
Industrial production is reaching a global tipping point. Moving past niche markets, Additive Manufacturing (AM)—commonly known as 3D printing—is revolutionizing how the world makes things.
Unlike traditional subtractive methods like milling or machining that cut material away, AM builds parts layer by layer from digital models. This approach is not just a novel technological trick; it is a fundamental shift that allows for lighter, stronger components and incredibly intricate systems that were previously impossible to manufacture.
Fueled by rapid advancements in machine speed, material diversity, and software accuracy, AM is now mainstream. For Malaysia, a global manufacturing hub, embracing this shift is crucial. Aligned with government initiatives promoting Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG), additive manufacturing offers a pathway to sustainable, high-value economic growth.
Here is a deep dive into the ecosystem of additive manufacturing in Malaysia and the opportunities it presents.
The Sustainability Edge: AM and ESG
Beyond sheer speed, additive manufacturing is a cornerstone of modern sustainable manufacturing strategies. It directly addresses key ESG goals:
Enhanced Product Design: Engineers can design stronger structures using significantly less material, often consolidating complex assemblies into single, robust components.
Streamlined Manufacturing: AM inherently reduces scrap waste. It promotes the reuse of surplus powder and aligns manufacturing processes with circular economy principles.
Agile Supply Chains: 3D printing enables on-demand production closer to the point of consumption. This decentralization drastically reduces carbon emissions from logistics and minimizes costly physical inventory.
Global Growth and the Malaysian Opportunity
The trajectory of 3D printing is undeniable. The global additive manufacturing market has been projected to grow at an annualized rate of 15%, surging from $5.31B in 2015 to an estimated $21.50B by 2025. Currently, the aerospace, automotive, and medical sectors dominate more than half of this market.
Why Malaysia Must Act Now
Malaysia has already proven its resilience. Despite pandemic challenges, local industries successfully leveraged 3D printing for mass customization and rapid response.
However, to maintain competitiveness globally, Malaysia must accelerate its transition from traditional methods to high-value, innovation-driven production. Key sectors—including automotive, medical devices, aviation, and electronics—face a critical juncture: adopt additive manufacturing or risk losing ground to regional competitors.
With modern AM technology moving far beyond prototyping into full-scale production, Malaysia stands to transform its entire production value chain. The Malaysian Investment Development Authority (MIDA) is strategically positioned to support this transition, helping industries boost efficiency, profitability, and high-value output.
The Core Pillars of Malaysia’s AM Ecosystem
A thriving additive manufacturing ecosystem relies on four interdependent components: hardware, materials, software, and service providers.
1. Manufacture of 3D Printers (Hardware)
The market has seen a surge in system manufacturers leading technological advancements. These solutions generally fall into two categories:
Industrial Grade Systems: High-end machines designed for mass production and heavy-duty applications in aerospace and automotive.
Desktop 3D Printers: Accessible, smaller-footprint machines used for rapid prototyping, education, and small-batch customizing.
2. Manufacture of Materials
The versatility of 3D printing is defined by its materials. The range of raw materials available in the Malaysian ecosystem is expanding rapidly:
Polymers (Plastics): The most common entry point. Thermoplastic powders and filaments are popular due to their cost-effectiveness and user-friendly properties for standard parts.
Metals: For applications demanding superior strength, heat resistance, and durability. Common materials include stainless steel, titanium, aluminium, and even precious metals like gold and silver.
Niche and Advanced Materials:
Biomaterials: Specialized materials like silicon, calcium phosphate, and zinc play a pivotal role in the medical field for bone reconstruction and tissue engineering.
Ceramics: Materials like zirconia and alumina are increasingly adopted for high-performance applications requiring heat and chemical resistance.
3. Software for 3D Printers
Software is the digital backbone of AM. It translates complex 3D CAD model data into essential instructions (G-code) that guide the printer layer by layer during production.
4. 3D Printing Services
Not every company needs to own industrial printers. A robust service sector is vital. This ranges from individual operators with desktop setups to large-scale service bureaus offering extensive industrial capabilities, post-processing, and global supply chain reach.

Government Policy: The Catalyst for Growth
Malaysia’s government recognizes AM as a vital component of its future economy, creating a supportive ecosystem through key national policies.
Industry4WRD: National Policy on Industry 4.0
Spanning 2018 to 2025, Industry4WRD is the blueprint for revolutionizing Malaysia’s manufacturing sector. Additive manufacturing is highlighted as one of the key technology pillars within this strategy, with specific incentives designed to promote its adoption across SMEs and MNCs alike.
Conclusion
Adopting additive manufacturing is no longer optional; it is crucial for Malaysia to maintain its status as a competitive global manufacturing hub. By leveraging this technology, Malaysia can unlock sustainable economic growth, access new international markets, and secure its leadership in the era of Industry 4.0.