Top Heat-Resistant Plastics for Industry
If you have ever left a plastic food container in the microwave for too long, you have likely seen firsthand that not all plastics are built to handle heat.
Many everyday containers are made from materials like polypropylene (PP), polyethylene (PE), or polycarbonate (PC). While these plastics work well for general use, they quickly reach their limits at elevated temperatures.
For example, polypropylene begins to lose strength at around 82°C (180°F). Polyethylene performs slightly better, tolerating temperatures up to 130°C (266°F). Even polycarbonate—often marketed as a “high-heat” plastic—typically maxes out at about 140°C (284°F). For applications that involve sustained or extreme heat, these materials simply are not enough.
This is where high-performance, heat-resistant plastics come into play. Materials such as PEEK, PTFE (Teflon), and Polyetherimide (PEI) are engineered to maintain their strength, stability, and performance in demanding thermal environments. These plastics are widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and medical devices, where reliability is critical.
What Is a Heat-Resistant Plastic?
Heat-resistant plastics are engineered materials specifically designed to perform reliably at high working temperatures without losing structural integrity.
For most industrial applications, this generally means continuous operating temperatures above 350°F (177°C); however, the exact requirements vary depending on the specific use case. It is therefore essential to distinguish between working temperature and melting temperature. While a plastic may not melt until reaching extremely high temperatures, it can begin to soften, deform, or lose mechanical strength well before that point.
Consequently, heat resistance emphasizes how well a material performs under real-world conditions, rather than merely its melting threshold.
Furthermore, another common misconception is that flame retardancy automatically equates to heat resistance. Although flame-retardant additives can reduce the risk of ignition, they frequently lower a material’s heat deflection and softening temperatures. For example, ABS plastic has a relatively low heat deflection temperature, and the addition of flame-retardant compounds can further reduce it—even though the material becomes less flammable. Therefore, when selecting a heat-resistant plastic, it is crucial to consider not only flame retardancy but also actual performance at elevated temperatures, mechanical stability, and long-term reliability.
Which Plastics Are Heat Resistant for Industrial Use?
Teflon®: “Making Things Better” at High Temperatures
One of the most well-known heat-resistant plastics is polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly known as Teflon. Discovered by accident in 1938, PTFE can withstand continuous service temperatures of up to 500°F (280°C).
PTFE is valued not only for its heat resistance but also for its exceptional chemical stability. It resists most acids, solvents, and corrosive substances, repels water, and has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material. This makes it extremely slippery and ideal for applications involving movement or wear.
PTFE is commonly used in mechanical components such as bearing blocks, seals, and housings. It is easy to machine and dimensionally stable, but it does have limitations. Because PTFE does not flow like typical thermoplastics when heated, it cannot be injection molded or 3D printed using standard methods.
PEEK: High Performance with Versatility
Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) is another standout heat-resistant plastic, offering an excellent balance of strength, temperature resistance, and processability. PEEK maintains its mechanical properties at temperatures up to 482°F (250°C) and has a melting point close to that of PTFE.
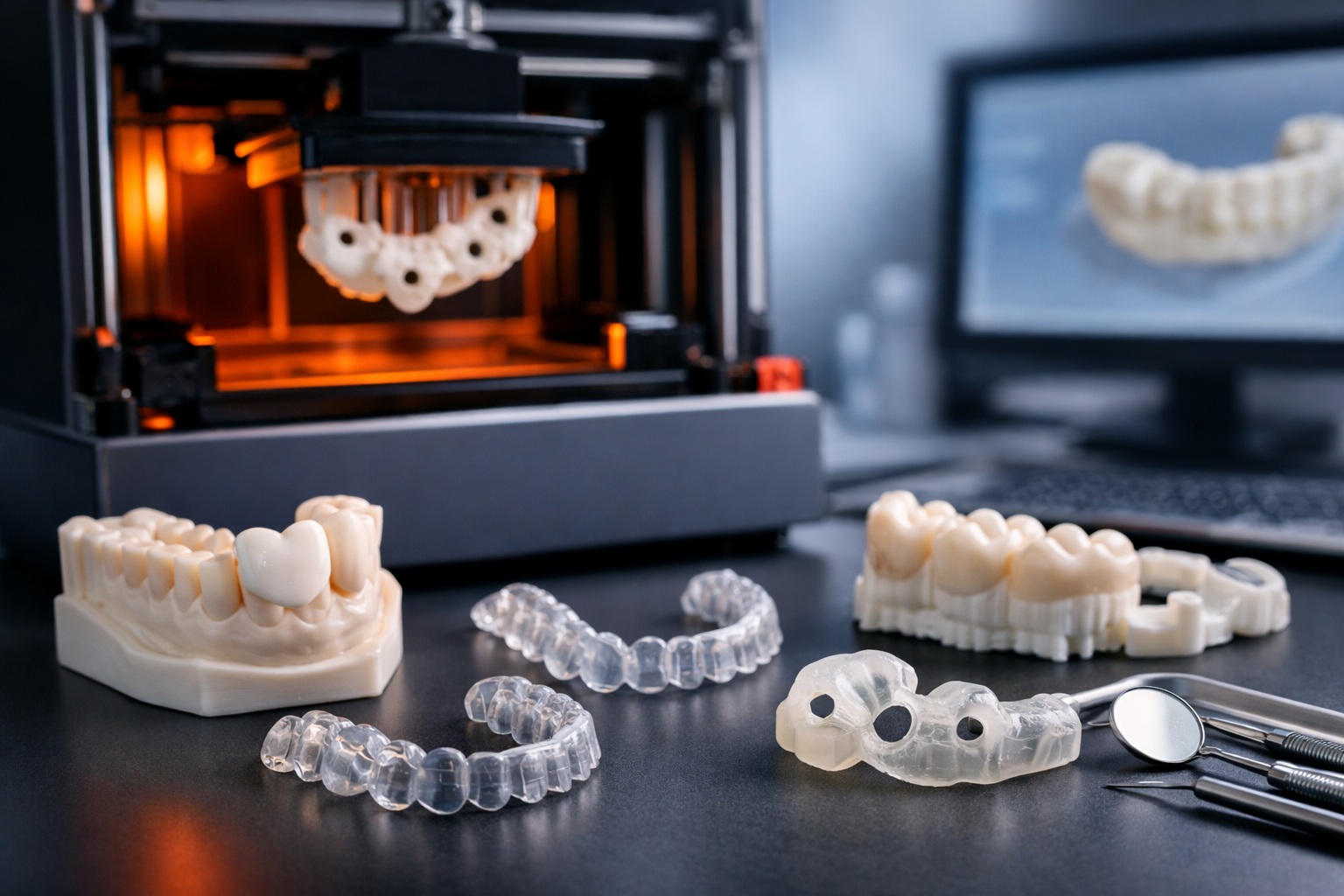
Unlike PTFE, PEEK can be injection molded, machined, and 3D printed using specialized equipment. It is resistant to chemicals, radiation, and hydrolysis, meaning it can be sterilized repeatedly in an autoclave. This makes it especially popular in medical applications such as spinal implants and surgical instruments.
PEEK also has a high strength-to-weight ratio and is frequently used as a lightweight replacement for metal components in aerospace and automotive applications. While it does not offer PTFE’s low friction, it excels in wear resistance and durability.
Heat-Resistant Materials for 3D Printing
As additive manufacturing continues to advance, an increasing number of heat-resistant plastics are becoming available for 3D printing. Consequently, for applications involving extreme or long-term heat exposure, advanced materials such as PEEK, PEI (Ultem), and PPSU not only withstand temperatures up to 250°C, but they also provide exceptional mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and durability. Furthermore, these high-performance polymers are increasingly used in demanding industrial parts, and as a result, engineers and manufacturers can rely on them for critical applications where traditional materials would fail.
For mid-range heat resistance, materials like polycarbonate (PC), nylon (PA), and ABS/ASA provide strong and durable options for functional components. PETG offers a more budget-friendly alternative for moderate heat applications, typically handling temperatures between 80°C and 90°C.
SLA 3D printing also offers high-temperature solutions. Ceramic-filled resins can withstand temperatures up to 280°C and are ideal for tooling, molds, and high-performance prototypes. Flame-retardant resins such as FR940 meet UL 94 V-0 standards and are widely used in electronics, automotive housings, and safety-critical components.
How to Choose the Right Heat-Resistant Plastic
Selecting the right heat-resistant plastic involves much more than simply considering temperature ratings. In addition, designers must evaluate mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and wear performance to ensure durability. Furthermore, factors such as the chosen manufacturing method and overall cost play a critical role in material selection. Therefore, by carefully balancing thermal properties, mechanical requirements, and production considerations, engineers can make informed decisions that maximize performance, efficiency, and long-term reliability.
Understanding the operating environment and performance requirements is key. By carefully matching material properties to application needs, manufacturers can ensure durability, safety, and long-term reliability—even in the most demanding conditions.
Comparison of Common Heat-Resistant Plastics
Material | Max Continuous Working Temperature* | Key Properties | Typical Applications | Manufacturing Compatibility |
PTFE (Teflon) | ~280°C (500°F) | Excellent chemical resistance, very low friction, hydrophobic | Bearings, seals, chemical components, coatings | CNC machining (not injection moldable or 3D printable) |
PEEK | ~250°C (482°F) | High strength, wear-resistant, lightweight, sterilizable | Medical implants, aerospace parts, automotive seals | CNC machining, injection molding, high-temp 3D printing |
PEI (Ultem) | ~217°C (423°F) | High stiffness, flame-retardant, good electrical insulation | Electronics housings, aerospace interiors | CNC machining, injection molding, 3D printing |
PPS (Polyphenylene Sulfide) | ~220°C (428°F) | Excellent chemical resistance, dimensional stability | Automotive parts, chemical processing | Injection molding, CNC machining |
PPSU | ~220–240°C | Tough, impact-resistant, autoclavable | Medical devices, food-contact parts | Injection molding, 3D printing |
Polycarbonate (PC) | ~140°C (284°F) | Tough, transparent, impact-resistant | Electrical enclosures, protective covers | Injection molding, CNC machining, 3D printing |
Nylon (PA) | ~120–170°C | Good strength, wear resistance, flexible grades | Gears, housings, industrial components | Injection molding, CNC machining, 3D printing |
ABS / ASA | ~95–105°C | Easy to process, cost-effective | Consumer products, prototypes | Injection molding, CNC machining, 3D printing |
PETG | ~80–90°C | Affordable, easy to print, moderate heat resistance | Prototypes, light-use parts | 3D printing |
3D Printing Service Malaysia , 3D Printing service Singapore , 3D Printing service KL , 3D Printing service Selangor, 3D Scanning Malaysia
Why Partner with Projet ?
Selecting the right manufacturing technology is important—but choosing the right manufacturing partner is what truly drives success. Companies across the electronics, automotive, consumer products, aerospace, and medical industries trust Projet because we are more than just a supplier; we are a dedicated partner in their success.
Here’s what sets us apart:
A True One-Stop Solution
We provide a seamless experience by offering a comprehensive suite of manufacturing services under one roof. This integrated approach streamlines your supply chain and simplifies the journey from concept to a market-ready product.
Engineering Expertise You Can Count On
Our experienced engineering team acts as a dedicated extension of your own. We excel at solving complex manufacturing challenges and collaborate closely with you to optimize your designs for quality, cost-effectiveness, and manufacturability.
Flexible Production Volumes to Match Your Needs
Whether you require a single prototype or a high-volume production run, our manufacturing capabilities are designed to scale with your demands. We support your product’s entire lifecycle, from initial launch to full-scale production.
Rapid Turnaround for a Faster Time-to-Market
In today’s fast-paced market, speed is a crucial advantage. We deliver fast, transparent quotes and pride ourselves on our rapid turnaround times, helping you get your innovative products to market sooner.
3D Printing Services
Instant Price