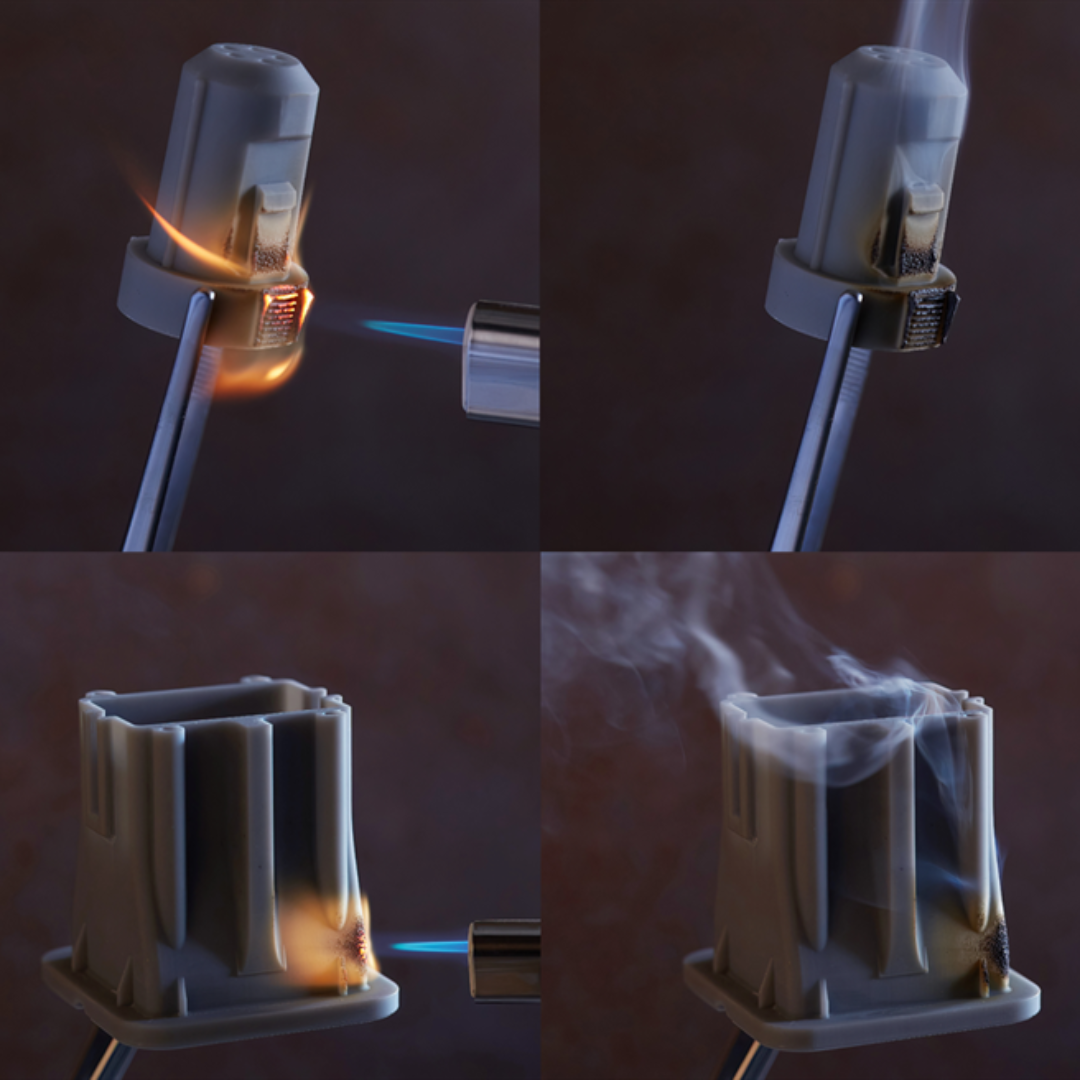
In industries like electronics, aerospace, and automotive, fire safety is a critical concern. As additive manufacturing (AM), commonly known as 3D printing, continues to transform production processes, selecting the right flame-retardant thermoplastics is essential to ensure safety, compliance, and reliability.
What is UL 94?
UL 94 is a widely recognized flammability standard for plastics, established by Underwriters Laboratories (UL) in the USA. It evaluates and classifies plastics based on their burning behavior in different orientations and thicknesses. The standard includes six classifications, ranging from the least to the most flame-retardant materials, helping manufacturers choose the right materials to meet fire safety requirements.
| UL 94 Rating | Definition of Rating |
| HB | Slow burning on a horizontal part. |
| V-2 | Burning stops within 30 seconds on a vertical part, with flaming drips |
| V-1 | Burning stops within 30 seconds on a vertical part, without flaming drips |
| V-0 | Burning stops within 10 seconds on a vertical part, without flaming drips. |
| 5VB | Burning stops within 60 seconds on a vertical part, without flaming drips. Burn-through (holes) may be present. |
| 5VA | Burning stops within 60 seconds on a vertical part, without flaming drips. No burn-through (no holes). |
The following table compares the attributes of UL 94 V-0 and HB ratings:
When discussing UL 94 flame classifications, the HB and V-0 ratings are frequently used. The key differences lie in the test orientation (horizontal vs. vertical) and the level of flame resistance required.
HB Rating: Measures the burn rate to meet specific standards but does not guarantee that the material will self-extinguish once the flame is removed.
V-0 Rating: Ensures the material self-extinguishes quickly, making it suitable for high-risk environments.
| Criteria | UL 94 HB attributes | UL 94 V-0 attributes |
| Flame retardant process | No advanced additives: Longer to put out fires, may drip or spread flames. | High-efficiency additives: Quickly extinguishes flames, prevents fire spread. |
| Effect on physical properties | More noticeable changes: Heat exposure can weaken the material. | Minor changes: Slight impact on strength or flexibility. |
| Compliance with safety norms | Meets basic flame resistance standards but may fall short for stringent fire safety demands. | Complies with the most demanding fire safety norms, ideal for high-risk environments. |
Why Choose the Right Rating?
Selecting the appropriate UL 94 rating depends on your application and industry requirements. For example:
HB-rated materials are suitable for low-risk applications where basic flame resistance is sufficient.
V-0-rated materials are ideal for high-risk environments, such as aerospace or automotive, where stringent fire safety standards are mandatory.
By understanding these classifications, manufacturers can make informed decisions to ensure safety, compliance, and reliability in their additive manufacturing processes.
Industrial Applications of Flame Retardant Materials
Automotive Industry
Flame-retardant materials play a crucial role in the automotive industry by ensuring compliance with fire safety regulations. These materials, such as flame-retardant ABS plastics, are commonly used in interior components like dashboards, upholstery, and wiring harnesses. By reducing the risk of fire during collisions or electrical malfunctions, they enhance vehicle safety and durability.
Electronics Industry
Flame-retardant materials are critical in electronics to protect sensitive components and ensure products comply with fire safety standards. These materials are widely used in circuit boards, connectors, and housing materials to minimize fire-related failures and electrical malfunctions, enhancing both safety and longevity.
Consumer Products
Flame-retardant materials are also found in everyday consumer goods such as furniture, appliances, and electronics. For instance, flame-retardant materials in upholstered furniture and bedding help prevent ignition and slow down fire spread, providing an extra layer of safety in homes and workplaces.
Collaborate with 3D printing bureau to choose the best material and optimize build orientation for your project’s needs. Explore our 3D Printing Materials Guide to learn about various plastic and metal materials across technologies.
Discover more about additive manufacturing at projet.my. For assistance, reach out to our applications engineer at enquiry@projettech.com or +604-2858 335.