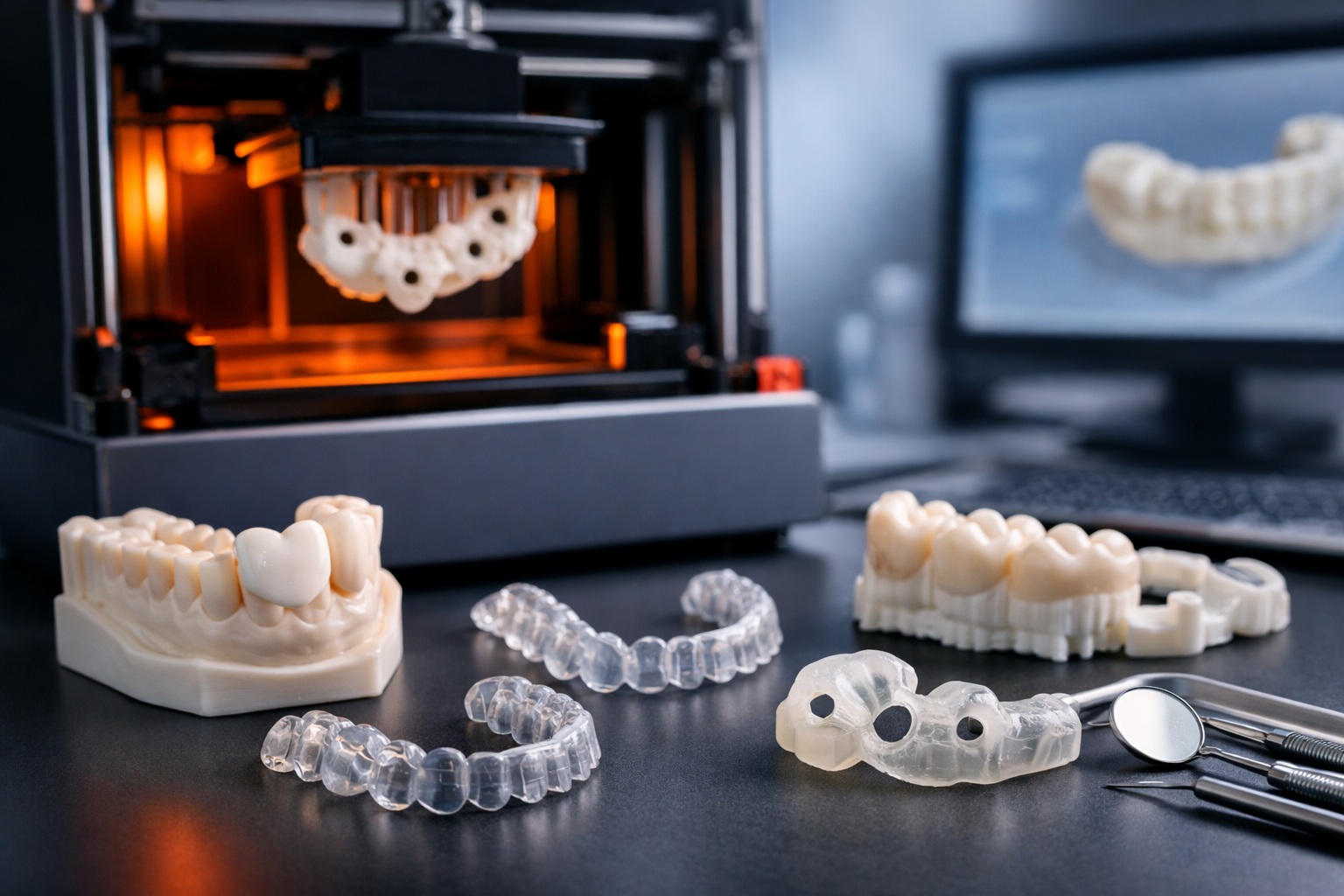
What is Micro 3D Printing ?
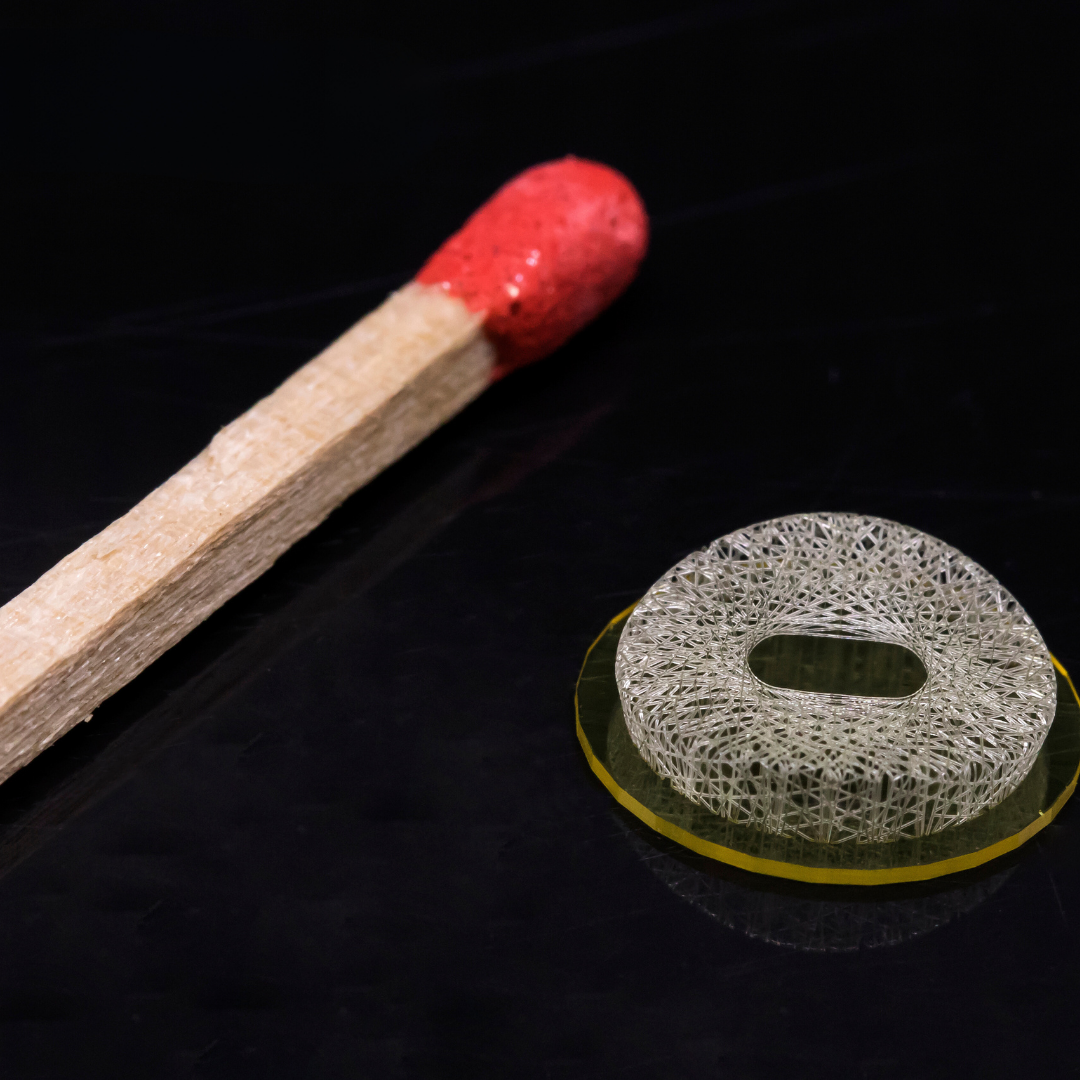
Micro 3D printing, also referred to as micromanufacturing or micro additive manufacturing (Micro AM), produces parts with micron-scale features. As an emerging technology, it is increasingly being recognized as a viable alternative to traditional manufacturing processes.
Types of Mirco 3D printing technologies
Micro Stereolithography (µSLA):
This technique falls under vat polymerization and involves curing photosensitive liquid resin with an ultraviolet laser. The process mirrors that of most commercial resin printers: resin is poured into a tank, a build platform is submerged, and a laser traces each layer of the 3D part as the platform descends. Unlike standard methods, µSLA utilizes advanced resins and lasers, along with precision lenses, to create incredibly small light points.
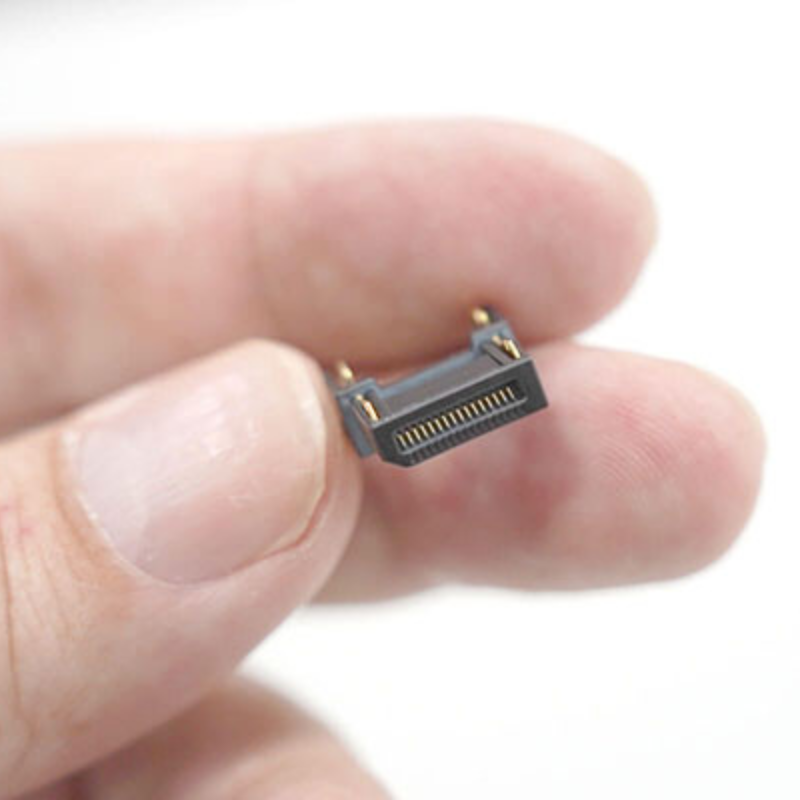

Projection Micro Stereolithography (PµSL):
Projection Microstereolithography (PµSL) is a rapidly advancing additive manufacturing technique known for its cost-effectiveness, precision, speed, and material versatility, including polymers, biomaterials, and ceramics. Promising for applications like microfluidics and tissue engineering, PµSL operates similarly to µSLA but uses UV light from a projector instead of a laser. This method, akin to digital light processing (DLP) technology, allows for swift photopolymerization of entire layers at micro-scale resolutions.
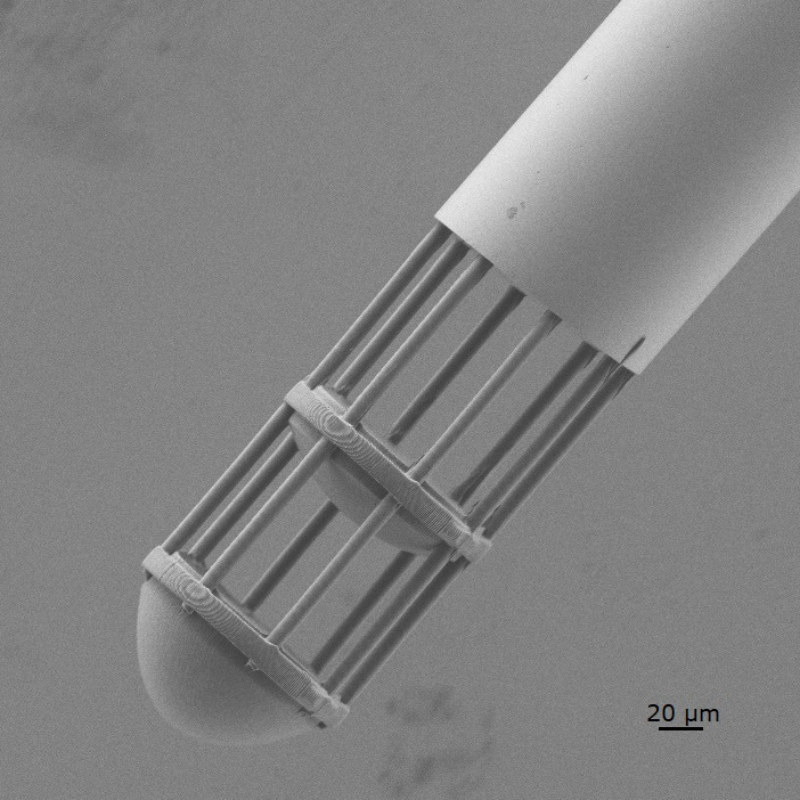
Two-Photon Polymerization (2PP or TPP):
This technology offers unparalleled accuracy among micro 3D printers and is used for advanced medical innovations, such as tissue engineering and implants, as well as for industrial micromechanics. However, it remains costly, and the printers can be slower compared to other technologies. This method employs a pulsed femtosecond laser to create 3D patterns within a vat of specialized photosensitive resin. While we won’t delve into the detailed science of photon interactions, it’s worth noting that this technology achieves resolutions under 1µm, qualifying it as a nanofabrication technique.
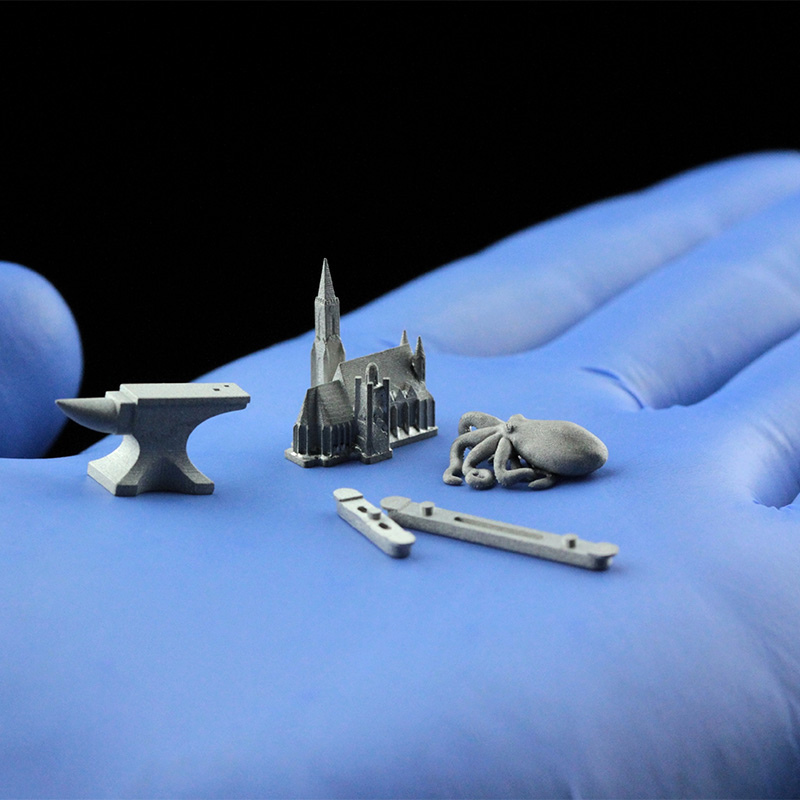

Lithography-based Metal Manufacturing (LMM):
This innovative metal 3D printing method produces small components for applications like surgical tools, utilizing principles similar to photopolymerization. Laser Metal Microfabrication (LMM) combines metal powder with light-sensitive resin, polymerized by blue light. After removing the polymer, “brown” parts are sintered in a furnace, employing materials such as stainless steel, titanium, tungsten, brass, copper, silver, and gold.
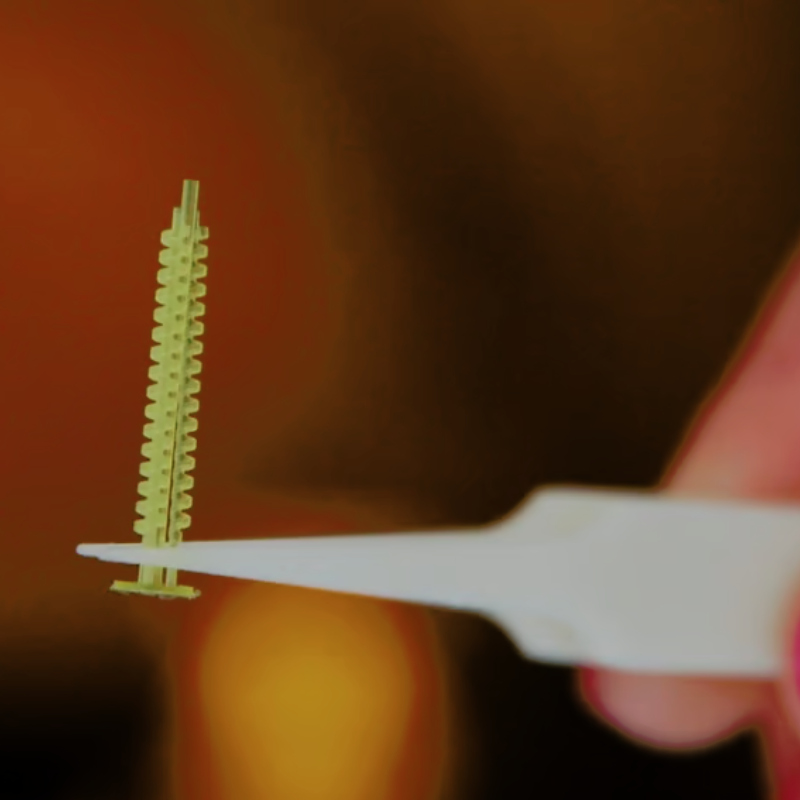
Micro Selective Laser Sintering (μSLS):
Micro laser sintering (μSLS) is a refined powder bed fusion method specifically for metals, unlike its counterpart selective laser sintering (SLS), which focuses on plastics. The process begins with a uniform layer of metal nanoparticle ink applied to a substrate, followed by drying. A laser, guided by a digital micromirror array, then sinters the nanoparticles into desired shapes, layer by layer, to create the final 3D part.
Applications of Micro 3D Printing:
- electrical components
- microchip components
- microfluidic devices
- drug-delivery microneedles
- vascular stents
- micro-scale molds
- electro-mechanical parts for optics & photonics
Connect with Projet:
If you’ve had a positive experience with Projet that you’d like to share, please reach out to us at enquiry@projettech.com. We eagerly anticipate hearing from you.
For additional information, visit our website for comprehensive details about our services and contact information. Our friendly team is ready to assist you at any time.